Linear Rail System SBI… - Romani GmbH
Linear Rail System SBI… - Romani GmbH
Linear Rail System SBI… - Romani GmbH
Sie wollen auch ein ePaper? Erhöhen Sie die Reichweite Ihrer Titel.
YUMPU macht aus Druck-PDFs automatisch weboptimierte ePaper, die Google liebt.
56<br />
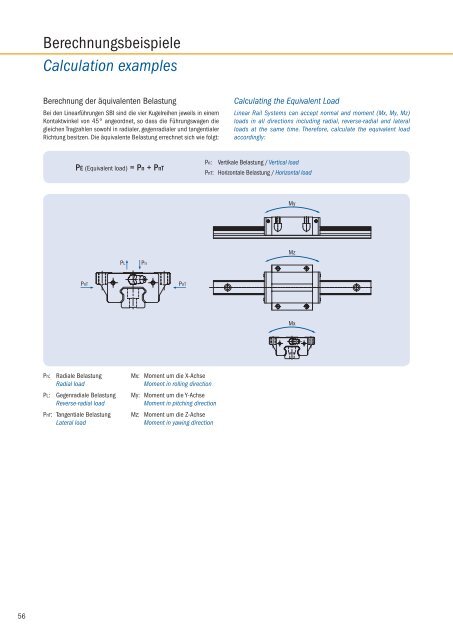
Berechnungsbeispiele<br />
Calculation examples<br />
Berechnung der äquivalenten Belastung<br />
Bei den <strong>Linear</strong>führungen SBI sind die vier Kugelreihen jeweils in einem<br />
Kontaktwinkel von 45° angeordnet, so dass die Führungswagen die<br />
gleichen Tragzahlen sowohl in radialer, gegenradialer und tangentialer<br />
Richtung besitzen. Die äquivalente Belastung errechnet sich wie folgt:<br />
PE (Equivalent load) = Pn + PnT<br />
PnT<br />
Pn: Radiale Belastung<br />
Radial load<br />
PL: Gegenradiale Belastung<br />
Reverse-radial load<br />
PnT: Tangentiale Belastung<br />
Lateral load<br />
PL Pn<br />
PnT<br />
Mx: Moment um die X-Achse<br />
Moment in rolling direction<br />
My: Moment um die Y-Achse<br />
Moment in pitching direction<br />
Mz: Moment um die Z-Achse<br />
Moment in yawing direction<br />
Calculating the Equivalent Load<br />
<strong>Linear</strong> <strong>Rail</strong> <strong>System</strong>s can accept normal and moment (Mx, My, Mz)<br />
loads in all directions including radial, reverse-radial and lateral<br />
loads at the same time. Therefore, calculate the equivalent load<br />
accordingly:<br />
Pn: Vertikale Belastung / Vertical load<br />
PnT: Horizontale Belastung / Horizontal load<br />
My<br />
Mz<br />
Mx