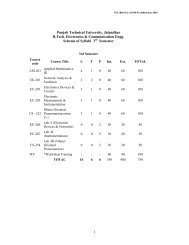
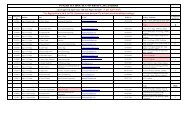
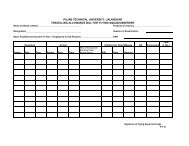
Revised scheme for B.Tech. - Punjab Technical University
Revised scheme for B.Tech. - Punjab Technical University
Revised scheme for B.Tech. - Punjab Technical University
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
PTU/BOS/ME/101/10-06-2005/BATCH-2003<br />
ME-201 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS – I<br />
Internal Marks: 40 L T P<br />
External Marks: 60 3 1 0<br />
Total Marks: 100<br />
Course Objectives<br />
1. Understand the concept of simple stress and strain.<br />
2. Understand different types of direct stresses and strains.<br />
3. Understand stress- strain diagram. Hookes law, Poisson’s ratio. Young’s<br />
Modulus of Elasticity.<br />
4. Compute simple stresses and strains in bars of uni<strong>for</strong>m and varying sections<br />
subjected to axial loads.<br />
5. Derive relationship between the Elastic Moduli.<br />
6. Compute stresses and strains in compound bars subjected to axial loads and<br />
temperature variations.<br />
7. Compute combined stresses and strains at a point across any plane in a two<br />
dimensional system.<br />
8. Understand the concept of principal planes and principal stresses.<br />
9. Apply graphical and analytical methods to compute principal stresses and strain<br />
and locate principal planes.<br />
10. Derive mathematically the Torsion Equation.<br />
11. Apply the Torsion equation to compute torsional stresses in solid and hollow<br />
shafts.<br />
12. Compute principal stresses and maximum shear stresses in circular shafts<br />
subjected to combined stresses.<br />
13. Analyze stresses in close- coiled helical springs.<br />
14. Analyze stresses in thin shells and spheres subjected to internal pressure.<br />
15. Apply different <strong>for</strong>mulae to analyze stresses in struts and columns subjected to<br />
axial loads.<br />
16. Compute bending moments and shear <strong>for</strong>ces at different sections of determinate<br />
beam structures subjected to different types of loading and sketch their<br />
distribution graphically.<br />
17. Derive mathematically the relationship between the rate of loading, shear <strong>for</strong>ce<br />
and bending moment at any section of a beam.<br />
18. Understand the theory of simple bending.<br />
19. Apply the theory of simple bending to compute stresses in beams of<br />
homogenous and composite sections of different shapes.<br />
20. Derive relationship between moment slope and deflection.<br />
21. Use the above relationship and other methods to calculate slope and deflection<br />
in beams.<br />
22. Compute stresses in determine trussed frames and roof trusses.<br />
Detailed Contents<br />
1. Simple stresses and strains : Concept of stress and strain; St. Vernants<br />
principle, stress and strain diagram, Hooke’s law, Young’s modulus, Poisson ratio,<br />
stress at a point, stress and strains in bars subjected to axial loading. Modulus of<br />
elasticity, stress produced in compound bars subject to axial loading.Temperature<br />
stress and strain calculations due to applications of axial loads and variation of<br />
temperature in single and compound bars. Compound stress and strains, the two<br />
dimensional system; stress at a point on a plane, principal stresses and principal<br />
planes; Mohr’s circle of stress; ellipse of stress and their applications. Generalized<br />
Hook's Law, principal stresses related to principal strains