The European Pharmaceutical Wholesale Industry: - phagro
The European Pharmaceutical Wholesale Industry: - phagro
The European Pharmaceutical Wholesale Industry: - phagro
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>The</strong> <strong>European</strong> <strong>Pharmaceutical</strong> <strong>Wholesale</strong> <strong>Industry</strong><br />
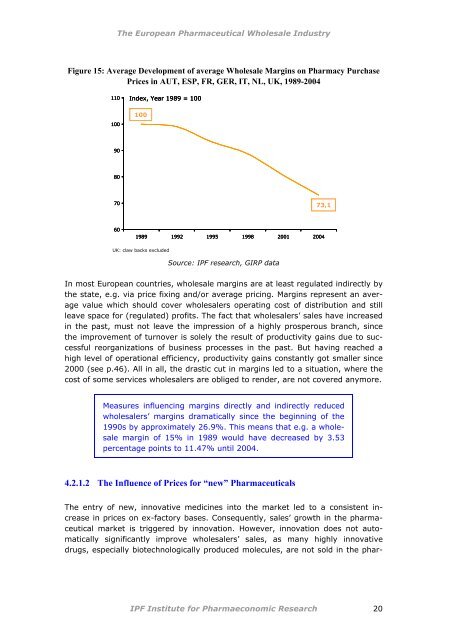
Figure 15: Average Development of average <strong>Wholesale</strong> Margins on Pharmacy Purchase<br />
Prices in AUT, ESP, FR, GER, IT, NL, UK, 1989-2004<br />
110<br />
100<br />
90<br />
80<br />
70<br />
60<br />
Index, Year 1989 = 100<br />
100<br />
73,1<br />
1989 1992 1995 1998 2001 2004<br />
UK: claw backs excluded<br />
Source: IPF research, GIRP data<br />
In most <strong>European</strong> countries, wholesale margins are at least regulated indirectly by<br />
the state, e.g. via price fixing and/or average pricing. Margins represent an average<br />
value which should cover wholesalers operating cost of distribution and still<br />
leave space for (regulated) profits. <strong>The</strong> fact that wholesalers’ sales have increased<br />
in the past, must not leave the impression of a highly prosperous branch, since<br />
the improvement of turnover is solely the result of productivity gains due to successful<br />
reorganizations of business processes in the past. But having reached a<br />
high level of operational efficiency, productivity gains constantly got smaller since<br />
2000 (see p.46). All in all, the drastic cut in margins led to a situation, where the<br />
cost of some services wholesalers are obliged to render, are not covered anymore.<br />
Measures influencing margins directly and indirectly reduced<br />
wholesalers’ margins dramatically since the beginning of the<br />
1990s by approximately 26.9%. This means that e.g. a wholesale<br />
margin of 15% in 1989 would have decreased by 3.53<br />
percentage points to 11.47% until 2004.<br />
4.2.1.2 <strong>The</strong> Influence of Prices for “new” <strong>Pharmaceutical</strong>s<br />
<strong>The</strong> entry of new, innovative medicines into the market led to a consistent increase<br />
in prices on ex-factory bases. Consequently, sales’ growth in the pharmaceutical<br />
market is triggered by innovation. However, innovation does not automatically<br />
significantly improve wholesalers’ sales, as many highly innovative<br />
drugs, especially biotechnologically produced molecules, are not sold in the phar-<br />
IPF Institute for Pharmaeconomic Research 20