Ground glass opacity on CT scanning of the chest: What does it mean?
Ground glass opacity on CT scanning of the chest: What does it mean?
Ground glass opacity on CT scanning of the chest: What does it mean?
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Causes <strong>of</strong> a diffuse pattern <strong>of</strong><br />
GGO <strong>on</strong> <strong>CT</strong> <strong>scanning</strong><br />
• Acute rejecti<strong>on</strong> <strong>of</strong> lung<br />
transplantati<strong>on</strong><br />
• Adult respiratory distress syndrome<br />
• Edema<br />
• Extrinsic allergic alveol<strong>it</strong>is<br />
• Hemorrhage<br />
• Infectious pneum<strong>on</strong>ia<br />
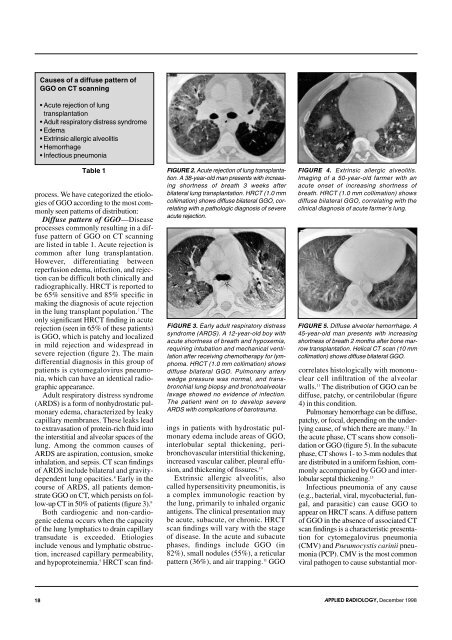
Table 1 FIGURE 2. Acute rejecti<strong>on</strong> <strong>of</strong> lung transplantati<strong>on</strong>.<br />
A 38-year-old man presents w<strong>it</strong>h increasing<br />
shortness <strong>of</strong> breath 3 weeks after<br />
process. We have categorized <strong>the</strong> etiologies<br />
<strong>of</strong> GGO according to <strong>the</strong> most comm<strong>on</strong>ly<br />
seen patterns <strong>of</strong> distributi<strong>on</strong>:<br />
Diffuse pattern <strong>of</strong> GGO—Disease<br />
processes comm<strong>on</strong>ly resulting in a diffuse<br />
pattern <strong>of</strong> GGO <strong>on</strong> <strong>CT</strong> <strong>scanning</strong><br />
are listed in table 1. Acute rejecti<strong>on</strong> is<br />
comm<strong>on</strong> after lung transplantati<strong>on</strong>.<br />
However, differentiating between<br />
reperfusi<strong>on</strong> edema, infecti<strong>on</strong>, and rejecti<strong>on</strong><br />
can be difficult both clinically and<br />
radiographically. HR<strong>CT</strong> is reported to<br />
be 65% sens<strong>it</strong>ive and 85% specific in<br />
making <strong>the</strong> diagnosis <strong>of</strong> acute rejecti<strong>on</strong><br />
in <strong>the</strong> lung transplant populati<strong>on</strong>. 7 The<br />
<strong>on</strong>ly significant HR<strong>CT</strong> finding in acute<br />
rejecti<strong>on</strong> (seen in 65% <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>se patients)<br />
is GGO, which is patchy and localized<br />
in mild rejecti<strong>on</strong> and widespread in<br />
severe rejecti<strong>on</strong> (figure 2). The main<br />
differential diagnosis in this group <strong>of</strong><br />
patients is cytomegalovirus pneum<strong>on</strong>ia,<br />
which can have an identical radiographic<br />
appearance.<br />
Adult respiratory distress syndrome<br />
(ARDS) is a form <strong>of</strong> n<strong>on</strong>hydrostatic pulm<strong>on</strong>ary<br />
edema, characterized by leaky<br />
capillary membranes. These leaks lead<br />
to extravasati<strong>on</strong> <strong>of</strong> protein-rich fluid into<br />
<strong>the</strong> interst<strong>it</strong>ial and alveolar spaces <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
lung. Am<strong>on</strong>g <strong>the</strong> comm<strong>on</strong> causes <strong>of</strong><br />
ARDS are aspirati<strong>on</strong>, c<strong>on</strong>tusi<strong>on</strong>, smoke<br />
inhalati<strong>on</strong>, and sepsis. <strong>CT</strong> scan findings<br />
<strong>of</strong> ARDS include bilateral and grav<strong>it</strong>ydependent<br />
lung opac<strong>it</strong>ies. 8 Early in <strong>the</strong><br />
course <strong>of</strong> ARDS, all patients dem<strong>on</strong>strate<br />
GGO <strong>on</strong> <strong>CT</strong>, which persists <strong>on</strong> follow-up<br />
<strong>CT</strong> in 50% <strong>of</strong> patients (figure 3). 9<br />
Both cardiogenic and n<strong>on</strong>-cardiogenic<br />
edema occurs when <strong>the</strong> capac<strong>it</strong>y<br />
<strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> lung lymphatics to drain capillary<br />
transudate is exceeded. Etiologies<br />
include venous and lymphatic obstructi<strong>on</strong>,<br />
increased capillary permeabil<strong>it</strong>y,<br />
and hypoproteinemia. 5 HR<strong>CT</strong> scan find-<br />
bilateral lung transplantati<strong>on</strong>. HR<strong>CT</strong> (1.0 mm<br />
collimati<strong>on</strong>) shows diffuse bilateral GGO, correlating<br />
w<strong>it</strong>h a pathologic diagnosis <strong>of</strong> severe<br />
acute rejecti<strong>on</strong>.<br />
FiGURE 3. Early adult respiratory distress<br />
syndrome (ARDS). A 12-year-old boy w<strong>it</strong>h<br />
acute shortness <strong>of</strong> breath and hypoxemia,<br />
requiring intubati<strong>on</strong> and mechanical ventilati<strong>on</strong><br />
after receiving chemo<strong>the</strong>rapy for lymphoma.<br />
HR<strong>CT</strong> (1.0 mm collimati<strong>on</strong>) shows<br />
diffuse bilateral GGO. Pulm<strong>on</strong>ary artery<br />
wedge pressure was normal, and transbr<strong>on</strong>chial<br />
lung biopsy and br<strong>on</strong>choalveolar<br />
lavage showed no evidence <strong>of</strong> infecti<strong>on</strong>.<br />
The patient went <strong>on</strong> to develop severe<br />
ARDS w<strong>it</strong>h complicati<strong>on</strong>s <strong>of</strong> barotrauma.<br />
ings in patients w<strong>it</strong>h hydrostatic pulm<strong>on</strong>ary<br />
edema include areas <strong>of</strong> GGO,<br />
interlobular septal thickening, peribr<strong>on</strong>chovascular<br />
interst<strong>it</strong>ial thickening,<br />
increased vascular caliber, pleural effusi<strong>on</strong>,<br />
and thickening <strong>of</strong> fissures. 10<br />
Extrinsic allergic alveol<strong>it</strong>is, also<br />
called hypersens<strong>it</strong>iv<strong>it</strong>y pneum<strong>on</strong><strong>it</strong>is, is<br />
a complex immunologic reacti<strong>on</strong> by<br />
<strong>the</strong> lung, primarily to inhaled organic<br />
antigens. The clinical presentati<strong>on</strong> may<br />
be acute, subacute, or chr<strong>on</strong>ic. HR<strong>CT</strong><br />
scan findings will vary w<strong>it</strong>h <strong>the</strong> stage<br />
<strong>of</strong> disease. In <strong>the</strong> acute and subacute<br />
phases, findings include GGO (in<br />
82%), small nodules (55%), a reticular<br />
pattern (36%), and air trapping. 11 GGO<br />
FIGURE 4. Extrinsic allergic alveol<strong>it</strong>is.<br />
Imaging <strong>of</strong> a 50-year-old farmer w<strong>it</strong>h an<br />
acute <strong>on</strong>set <strong>of</strong> increasing shortness <strong>of</strong><br />
breath. HR<strong>CT</strong> (1.0 mm collimati<strong>on</strong>) shows<br />
diffuse bilateral GGO, correlating w<strong>it</strong>h <strong>the</strong><br />
clinical diagnosis <strong>of</strong> acute farmer’s lung.<br />
FIGURE 5. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage. A<br />
45-year-old man presents w<strong>it</strong>h increasing<br />
shortness <strong>of</strong> breath 2 m<strong>on</strong>ths after b<strong>on</strong>e marrow<br />
transplantati<strong>on</strong>. Helical <strong>CT</strong> scan (10 mm<br />
collimati<strong>on</strong>) shows diffuse bilateral GGO.<br />
correlates histologically w<strong>it</strong>h m<strong>on</strong><strong>on</strong>uclear<br />
cell infiltrati<strong>on</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> alveolar<br />
walls. 11 The distributi<strong>on</strong> <strong>of</strong> GGO can be<br />
diffuse, patchy, or centrilobular (figure<br />
4) in this c<strong>on</strong>d<strong>it</strong>i<strong>on</strong>.<br />
Pulm<strong>on</strong>ary hemorrhage can be diffuse,<br />
patchy, or focal, depending <strong>on</strong> <strong>the</strong> underlying<br />
cause, <strong>of</strong> which <strong>the</strong>re are many. 12 In<br />
<strong>the</strong> acute phase, <strong>CT</strong> scans show c<strong>on</strong>solidati<strong>on</strong><br />
or GGO (figure 5). In <strong>the</strong> subacute<br />
phase, <strong>CT</strong> shows 1- to 3-mm nodules that<br />
are distributed in a uniform fashi<strong>on</strong>, comm<strong>on</strong>ly<br />
accompanied by GGO and interlobular<br />
septal thickening. 13<br />
Infectious pneum<strong>on</strong>ia <strong>of</strong> any cause<br />
(e.g., bacterial, viral, mycobacterial, fungal,<br />
and paras<strong>it</strong>ic) can cause GGO to<br />
appear <strong>on</strong> HR<strong>CT</strong> scans. A diffuse pattern<br />
<strong>of</strong> GGO in <strong>the</strong> absence <strong>of</strong> associated <strong>CT</strong><br />
scan findings is a characteristic presentati<strong>on</strong><br />
for cytomegalovirus pneum<strong>on</strong>ia<br />
(CMV) and Pneumocystis carinii pneum<strong>on</strong>ia<br />
(PCP). CMV is <strong>the</strong> most comm<strong>on</strong><br />
viral pathogen to cause substantial mor-<br />
18 APPLIED RADIOLOGY, December 1998