Understanding Clinical Trial Design - Research Advocacy Network
Understanding Clinical Trial Design - Research Advocacy Network
Understanding Clinical Trial Design - Research Advocacy Network
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
UNDERSTANDING CLINICAL TRIAL DESIGN: A TUTORIAL FOR RESEARCH ADVOCATES<br />
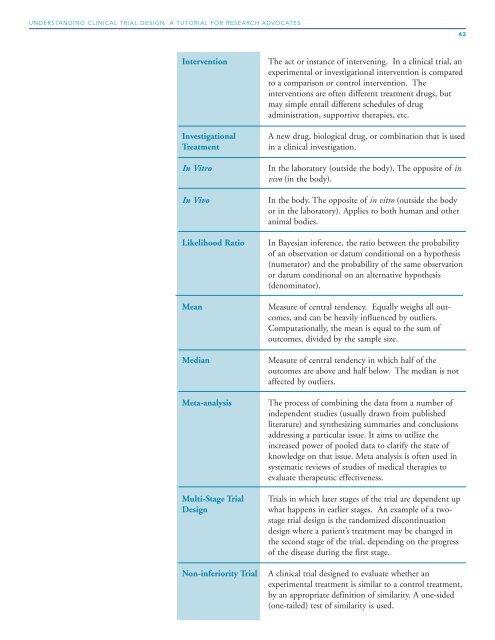
Intervention The act or instance of intervening. In a clinical trial, an<br />
experimental or investigational intervention is compared<br />
to a comparison or control intervention. The<br />
interventions are often different treatment drugs, but<br />
may simple entail different schedules of drug<br />
administration, supportive therapies, etc.<br />
Investigational A new drug, biological drug, or combination that is used<br />
Treatment in a clinical investigation.<br />
In Vitro In the laboratory (outside the body). The opposite of in<br />
vivo (in the body).<br />
In Vivo In the body. The opposite of in vitro (outside the body<br />
or in the laboratory). Applies to both human and other<br />
animal bodies.<br />
Likelihood Ratio In Bayesian inference, the ratio between the probability<br />
of an observation or datum conditional on a hypothesis<br />
(numerator) and the probability of the same observation<br />
or datum conditional on an alternative hypothesis<br />
(denominator).<br />
Mean Measure of central tendency. Equally weighs all outcomes,<br />
and can be heavily influenced by outliers.<br />
Computationally, the mean is equal to the sum of<br />
outcomes, divided by the sample size.<br />
Median Measure of central tendency in which half of the<br />
outcomes are above and half below. The median is not<br />
affected by outliers.<br />
Meta-analysis The process of combining the data from a number of<br />
independent studies (usually drawn from published<br />
literature) and synthesizing summaries and conclusions<br />
addressing a particular issue. It aims to utilize the<br />
increased power of pooled data to clarify the state of<br />
knowledge on that issue. Meta analysis is often used in<br />
systematic reviews of studies of medical therapies to<br />
evaluate therapeutic effectiveness.<br />
Multi-Stage <strong>Trial</strong> <strong>Trial</strong>s in which later stages of the trial are dependent up<br />
<strong>Design</strong> what happens in earlier stages. An example of a twostage<br />
trial design is the randomized discontinuation<br />
design where a patient’s treatment may be changed in<br />
the second stage of the trial, depending on the progress<br />
of the disease during the first stage.<br />
Non-inferiority <strong>Trial</strong> A clinical trial designed to evaluate whether an<br />
experimental treatment is similar to a control treatment,<br />
by an appropriate definition of similarity. A one-sided<br />
(one-tailed) test of similarity is used.<br />
43