utilizing physical layer information to improve rfid tag
utilizing physical layer information to improve rfid tag
utilizing physical layer information to improve rfid tag
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
2.1 RFID Reader<br />
CHAPTER 2<br />
PASSIVE UHF RFID SYSTEMS<br />
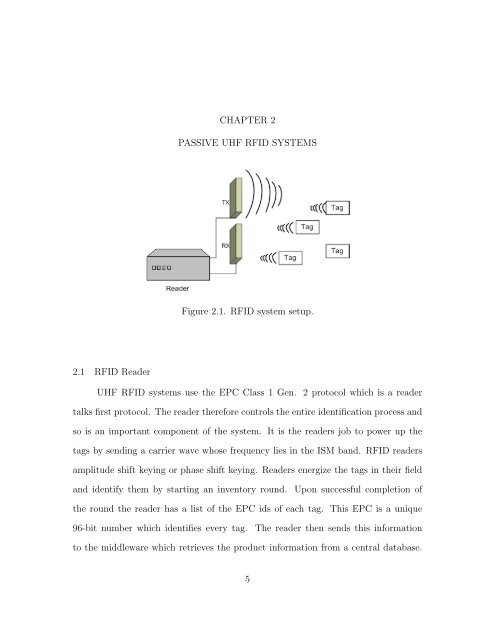
Figure 2.1. RFID system setup.<br />
UHF RFID systems use the EPC Class 1 Gen. 2 pro<strong>to</strong>col which is a reader<br />
talks first pro<strong>to</strong>col. The reader therefore controls the entire identification process and<br />
so is an important component of the system. It is the readers job <strong>to</strong> power up the<br />
<strong>tag</strong>s by sending a carrier wave whose frequency lies in the ISM band. RFID readers<br />
amplitude shift keying or phase shift keying. Readers energize the <strong>tag</strong>s in their field<br />
and identify them by starting an inven<strong>to</strong>ry round. Upon successful completion of<br />
the round the reader has a list of the EPC ids of each <strong>tag</strong>. This EPC is a unique<br />
96-bit number which identifies every <strong>tag</strong>. The reader then sends this <strong>information</strong><br />
<strong>to</strong> the middleware which retrieves the product <strong>information</strong> from a central database.<br />
5