Switched-Capacitor Circuits - University of Toronto
Switched-Capacitor Circuits - University of Toronto
Switched-Capacitor Circuits - University of Toronto
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
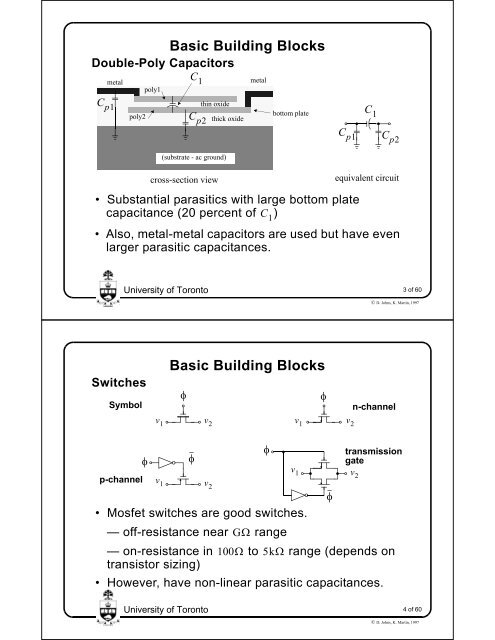
Double-Poly <strong>Capacitor</strong>s<br />
C p1<br />
metal<br />
poly2<br />
poly1<br />
<strong>University</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Toronto</strong><br />
Basic Building Blocks<br />
C 1<br />
C p2<br />
thin oxide<br />
(substrate - ac ground)<br />
cross-section view<br />
thick oxide<br />
metal<br />
bottom plate<br />
C p1<br />
• Substantial parasitics with large bottom plate<br />
capacitance (20 percent <strong>of</strong> )<br />
• Also, metal-metal capacitors are used but have even<br />
larger parasitic capacitances.<br />
Switches<br />
Symbol<br />
p-channel<br />
<br />
v 1<br />
v 1<br />
<strong>University</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Toronto</strong><br />
C 1<br />
Basic Building Blocks<br />
<br />
<br />
v 2<br />
v 2<br />
C 1<br />
C p2<br />
equivalent circuit<br />
3 <strong>of</strong> 60<br />
© D. Johns, K. Martin, 1997<br />
<br />
• Mosfet switches are good switches.<br />
— <strong>of</strong>f-resistance near G range<br />
— on-resistance in 100 to 5k<br />
range (depends on<br />
transistor sizing)<br />
• However, have non-linear parasitic capacitances.<br />
<br />
v 1<br />
v 1<br />
<br />
v 2<br />
n-channel<br />
transmission<br />
gate<br />
v 2<br />
4 <strong>of</strong> 60<br />
© D. Johns, K. Martin, 1997