The Biodiversity of Bac Huong Hoa Nature Reserve - Birdlife ...
The Biodiversity of Bac Huong Hoa Nature Reserve - Birdlife ...
The Biodiversity of Bac Huong Hoa Nature Reserve - Birdlife ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
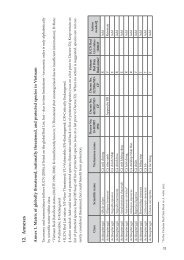
Land cover Area (ha) Proportion (%)<br />
Grass and scrub 861 3<br />
Rocky mountains without forest 889 4<br />
Other land uses* 580 2<br />
Total area 25,200 100<br />
*Other land uses includes agriculture, residential and water bodies<br />
2.8.1 High quality forest<br />
Although there is no primary forest in BHH NR, forest with a structure unaltered since 1975 is<br />
classified as rich forest and is broadly analogous to primary lowland forest in terms <strong>of</strong> species<br />
composition and structure. This forest type makes up less than 10% <strong>of</strong> BHH NR. It is distributed<br />
in the north <strong>of</strong> the nature reserve in two blocks situated close to Cup and Cuoi villages, close to<br />
the Ho Chi Minh Highway.<br />
Tropical lowland evergreen forest<br />
Below 600 m on soils with a low sand content, tropical lowland evergreen forest supports a<br />
diverse flora composed <strong>of</strong> broadleaf evergreen trees with large crowns and thick trunks. Trees in<br />
this habitat are from the families Meliaceae, Sapindaceae, Burceraceae, Eleocarpaceae,<br />
Myrtaceae, Ebenaceae, Annonaceae, Fabaceae, Fagaceae, Euphorbiaceae, Lauraceae,<br />
Simplocaceae, Sterculiaceae, Apocynaceae, Flacoutiaceae, Araliaceae, Rubiaceae and Moraceae.<br />
<strong>The</strong>se forests support many large lianas, some up to 30 metres long and 10 cm in diameter. <strong>The</strong>se<br />
are typically <strong>of</strong> the families Apocynaceae, Annonaceae, Fabaceae, Vitaceae, Aslepiadaceae and<br />
Arecaceae. Under the forest canopy small trees and bushes <strong>of</strong> the families Rubiaceae,<br />
Acanthaceae, Melastomataceae, Araliaceae, Arecaceae and Cyatheaceae are found. On the forest<br />
floor there are ferns from the families Polypodyophyta, Araceae, Urticaceae, Pandanaceae,<br />
Maranthaceae, Zingiberaceae, Commelinaceae and Myrsinaceae; and in light gaps flowers from<br />
the families Rubiaceae, Poaceae, Asteraceae and Begoniaceae grow. <strong>The</strong> layers in this forest type<br />
in BHH NR are detailed below:<br />
Emergent layer: This layer is characterised by large trees which can reach a height <strong>of</strong> 30 metres,<br />
although they are typically no more than 20-25 metres. Trees in this layer exhibit diameters <strong>of</strong><br />
40-80 cm, although some reach up to 120 cm. However, these large trees are relatively scarce and<br />
despite their size, this layer accounts for just 15-20% <strong>of</strong> the total area. Typical species on this<br />
layer are: Canarium subulatum, Canarium album, and trees from the family Burceraceae.<br />
Canopy layer: <strong>The</strong> canopy layer is dominated by trees <strong>of</strong> 10-15 metres. <strong>The</strong>se trees are relatively<br />
uniform in height; they have round canopies and trunks <strong>of</strong> 30-40 cm in diameter. <strong>The</strong>re is high<br />
species diversity in this layer and depending on location; the dominant families may be:<br />
Fagaceae, Lauraceae, Fabaceae, Meliaceae or Sapindaceae.<br />
Mid-story: This layer is dominated by small tree species <strong>of</strong> 7-10 m in height, and young<br />
specimens from the canopy and emergent layers. Typically, species are <strong>of</strong> the families<br />
Apocynaceae, Rubiaceae, Lauraceae, Euphorbiaceae, Myrtaceae, Araliaceae, Moraceae,<br />
Sapindaceae, Eleocarpaceae, Fagaceae, Flacourtiaceae, Annonaceae, Meliaceae, Rutaceae,<br />
20