Thermodynamic Quantities for the Ionization Reactions of Buffers
Thermodynamic Quantities for the Ionization Reactions of Buffers
Thermodynamic Quantities for the Ionization Reactions of Buffers
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
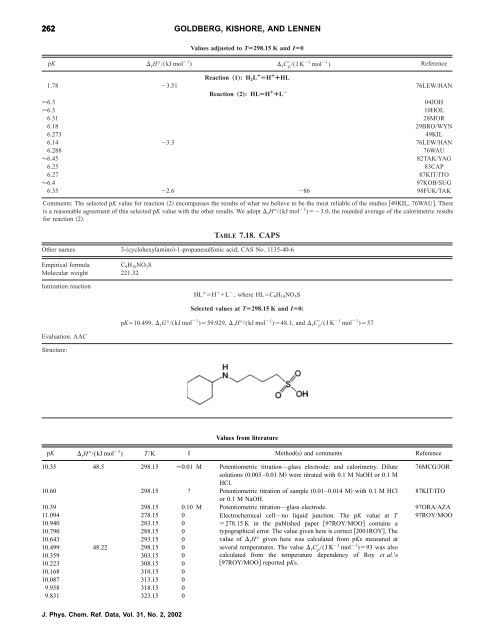
262 GOLDBERG, KISHORE, AND LENNEN<br />
Values adjusted to TÄ298.15 K and IÄ0<br />
pK rH°/(kJ mol 1 ) rC p /(J K 1 mol 1 ) Reference<br />
Reaction „1…: H2L ¿ ÄH ¿ ¿HL<br />
1.78 3.51 76LEW/HAN<br />
Reaction „2…: HLÄH ¿ ¿LÀ 6.3 04JOH<br />
6.3 10HOL<br />
6.31 28MOR<br />
6.18 29BRO/WYN<br />
6.273 49KIL<br />
6.14 3.3 76LEW/HAN<br />
6.288 76WAU<br />
6.45 82TAK/YAG<br />
6.25 83CAP<br />
6.27 87KIT/ITO<br />
6.4 97KOB/SUG<br />
6.35 2.6 86 98FUK/TAK<br />
Comments: The selected pK value <strong>for</strong> reaction 2 encompasses <strong>the</strong> results <strong>of</strong> what we believe to be <strong>the</strong> most reliable <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> studies 49KIL, 76WAU. There<br />
is a reasonable agreement <strong>of</strong> this selected pK value with <strong>the</strong> o<strong>the</strong>r results. We adopt rH°/(kJmol1 )3.0, <strong>the</strong> rounded average <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> calorimetric results<br />
<strong>for</strong> reaction 2.<br />
TABLE 7.18. CAPS<br />
O<strong>the</strong>r names 3-cyclohexylamino-1-propanesulfonic acid; CAS No. 1135-40-6<br />
Empirical <strong>for</strong>mula C 9H 19NO 3S<br />
Molecular weight 221.32<br />
<strong>Ionization</strong> reaction<br />
Evaluation: AAC<br />
Structure:<br />
HL H L , where HLC 9H 19NO 3S<br />
Selected values at TÄ298.15 K and IÄ0:<br />
pK10.499, rG°/(kJ mol 1 )59.929, rH°/(kJ mol 1 )48.1, and rC p /(J K 1 mol 1 )57<br />
Values from literature<br />
pK rH°/(kJ mol 1 ) T/K I Methods and comments Reference<br />
10.35 48.5 298.15 0.01 M Potentiometric titration—glass electrode; and calorimetry. Dilute<br />
solutions 0.005–0.01 M were titrated with 0.1 M NaOH or 0.1 M<br />
HCl.<br />
76MCG/JOR<br />
10.60 298.15 ? Potentiometric titration <strong>of</strong> sample 0.01–0.014 M with 0.1 M HCl<br />
or 0.1 M NaOH.<br />
87KIT/ITO<br />
10.39 298.15 0.10 M Potentiometric titration—glass electrode. 97ORA/AZA<br />
11.094 278.15 0 Electrochemical cell—no liquid junction. The pK value at T 97ROY/MOO<br />
10.940 283.15 0<br />
10.790 288.15 0<br />
10.643 293.15 0<br />
10.499 48.22 298.15 0<br />
10.359 303.15 0<br />
10.223 308.15 0<br />
10.168 310.15 0<br />
10.087 313.15 0<br />
9.958 318.15 0<br />
9.831 323.15 0<br />
J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, Vol. 31, No. 2, 2002<br />
278.15 K in <strong>the</strong> published paper 97ROY/MOO contains a<br />
typographical error. The value given here is correct 2001ROY. The<br />
value <strong>of</strong> rH° given here was calculated from pKs measured at<br />
several temperatures. The value rC p /(J K 1 mol 1 )93 was also<br />
calculated from <strong>the</strong> temperature dependency <strong>of</strong> Roy et al.’s<br />
97ROY/MOO reported pKs.