Mauritania - Islamic Development Bank
Mauritania - Islamic Development Bank
Mauritania - Islamic Development Bank
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
hotel business, and banking and insurance.<br />
Industry provides the second lead contribution<br />
(31%) followed by the primary sector (18%). The<br />
growth in industry hinges on the development<br />
of iron ore project, Guelb II, government<br />
investments in construction, electricity sector<br />
reform, and improvement in business climate.<br />
Agriculture sector, on the other hand, depends<br />
on improved irrigation and focused investment to<br />
develop livestock, fisheries, and rural businesses.<br />
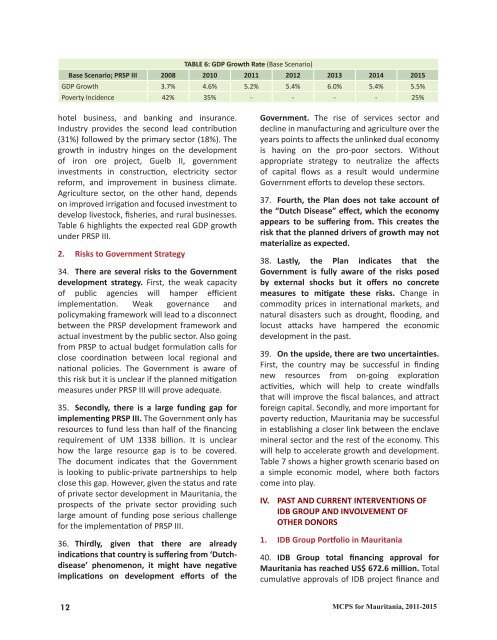
Table 6 highlights the expected real GDP growth<br />
under PRSP III.<br />
2. Risks to Government Strategy<br />
34. There are several risks to the Government<br />
development strategy. First, the weak capacity<br />
of public agencies will hamper efficient<br />
implementation. Weak governance and<br />
policymaking framework will lead to a disconnect<br />
between the PRSP development framework and<br />
actual investment by the public sector. Also going<br />
from PRSP to actual budget formulation calls for<br />
close coordination between local regional and<br />
national policies. The Government is aware of<br />
this risk but it is unclear if the planned mitigation<br />
measures under PRSP III will prove adequate.<br />
35. Secondly, there is a large funding gap for<br />
implementing PRSP III. The Government only has<br />
resources to fund less than half of the financing<br />
requirement of UM 1338 billion. It is unclear<br />
how the large resource gap is to be covered.<br />
The document indicates that the Government<br />
is looking to public-private partnerships to help<br />
close this gap. However, given the status and rate<br />
of private sector development in <strong>Mauritania</strong>, the<br />
prospects of the private sector providing such<br />
large amount of funding pose serious challenge<br />
for the implementation of PRSP III.<br />
36. Thirdly, given that there are already<br />
indications that country is suffering from ‘Dutchdisease’<br />
phenomenon, it might have negative<br />
implications on development efforts of the<br />
12<br />
TABLE 6: GDP Growth Rate (Base Scenario)<br />
Base Scenario; PRSP III 2008 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015<br />
GDP Growth 3.7% 4.6% 5.2% 5.4% 6.0% 5.4% 5.5%<br />
Poverty Incidence 42% 35% - - - - 25%<br />
Government. The rise of services sector and<br />
decline in manufacturing and agriculture over the<br />
years points to affects the unlinked dual economy<br />
is having on the pro-poor sectors. Without<br />
appropriate strategy to neutralize the affects<br />
of capital flows as a result would undermine<br />
Government efforts to develop these sectors.<br />
37. Fourth, the Plan does not take account of<br />
the “Dutch Disease” effect, which the economy<br />
appears to be suffering from. This creates the<br />
risk that the planned drivers of growth may not<br />
materialize as expected.<br />
38. Lastly, the Plan indicates that the<br />
Government is fully aware of the risks posed<br />
by external shocks but it offers no concrete<br />
measures to mitigate these risks. Change in<br />
commodity prices in international markets, and<br />
natural disasters such as drought, flooding, and<br />
locust attacks have hampered the economic<br />
development in the past.<br />
39. On the upside, there are two uncertainties.<br />
First, the country may be successful in finding<br />
new resources from on-going exploration<br />
activities, which will help to create windfalls<br />
that will improve the fiscal balances, and attract<br />
foreign capital. Secondly, and more important for<br />
poverty reduction, <strong>Mauritania</strong> may be successful<br />
in establishing a closer link between the enclave<br />
mineral sector and the rest of the economy. This<br />
will help to accelerate growth and development.<br />
Table 7 shows a higher growth scenario based on<br />
a simple economic model, where both factors<br />
come into play.<br />
IV. PAST AND CURRENT INTERVENTIONS OF<br />
IDB GROUP AND INVOLVEMENT OF<br />
OTHER DONORS<br />
1. IDB Group Portfolio in <strong>Mauritania</strong><br />
40. IDB Group total financing approval for<br />
<strong>Mauritania</strong> has reached US$ 672.6 million. Total<br />
cumulative approvals of IDB project finance and<br />
MCPS for <strong>Mauritania</strong>, 2011-2015