Silica (crystalline, respirable) - OEHHA
Silica (crystalline, respirable) - OEHHA
Silica (crystalline, respirable) - OEHHA
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
FINAL February 2005<br />
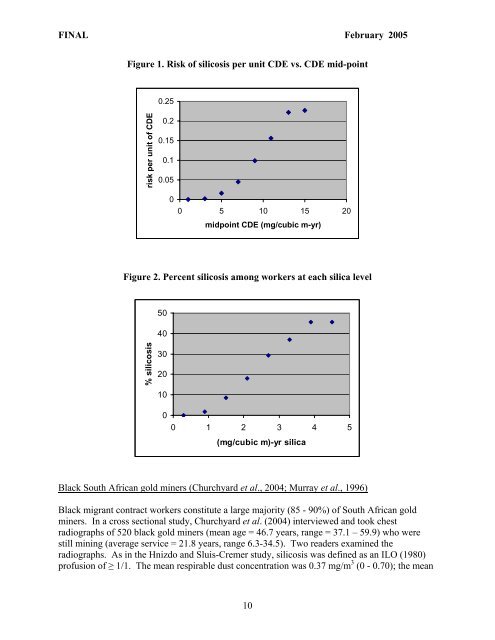
Figure 1. Risk of silicosis per unit CDE vs. CDE mid-point<br />
risk per unit of CDE<br />
0.25<br />
0.2<br />
0.15<br />
0.1<br />
0.05<br />
0<br />
0 5 10 15 20<br />
midpoint CDE (mg/cubic m-yr)<br />
Figure 2. Percent silicosis among workers at each silica level<br />
% silicosis<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
0<br />
0 1 2 3 4 5<br />
(mg/cubic m)-yr silica<br />
Black South African gold miners (Churchyard et al., 2004; Murray et al., 1996)<br />
Black migrant contract workers constitute a large majority (85 - 90%) of South African gold<br />
miners. In a cross sectional study, Churchyard et al. (2004) interviewed and took chest<br />
radiographs of 520 black gold miners (mean age = 46.7 years, range = 37.1 – 59.9) who were<br />
still mining (average service = 21.8 years, range 6.3-34.5). Two readers examined the<br />
radiographs. As in the Hnizdo and Sluis-Cremer study, silicosis was defined as an ILO (1980)<br />
profusion of ≥ 1/1. The mean <strong>respirable</strong> dust concentration was 0.37 mg/m 3 (0 - 0.70); the mean<br />
10