Consistent chiral three-nucleon interactions in ... - Theory Center
Consistent chiral three-nucleon interactions in ... - Theory Center
Consistent chiral three-nucleon interactions in ... - Theory Center
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
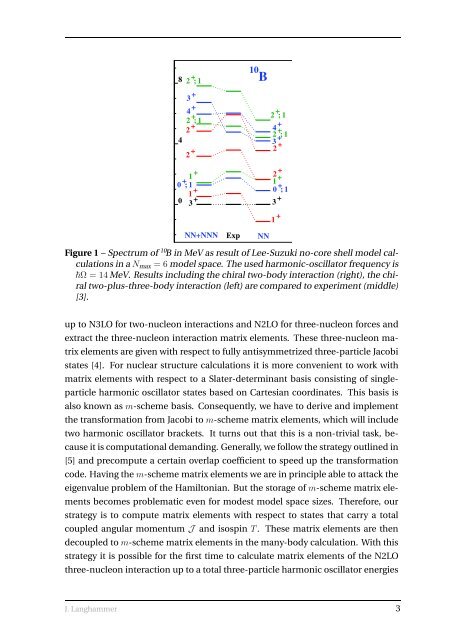
Figure 1 – Spectrum of 10 B <strong>in</strong> MeV as result of Lee-Suzuki no-core shell model calculations<br />
<strong>in</strong> a Nmax = 6 model space. The used harmonic-oscillator frequency is<br />
Ω = 14 MeV. Results <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g the <strong>chiral</strong> two-body <strong>in</strong>teraction (right), the <strong>chiral</strong><br />
two-plus-<strong>three</strong>-body <strong>in</strong>teraction (left) are compared to experiment (middle)<br />
[3].<br />
up to N3LO for two-<strong>nucleon</strong> <strong><strong>in</strong>teractions</strong> and N2LO for <strong>three</strong>-<strong>nucleon</strong> forces and<br />
extract the <strong>three</strong>-<strong>nucleon</strong> <strong>in</strong>teraction matrix elements. These <strong>three</strong>-<strong>nucleon</strong> ma-<br />
trix elements are given with respect to fully antisymmetrized <strong>three</strong>-particle Jacobi<br />
states [4]. For nuclear structure calculations it is more convenient to work with<br />
matrix elements with respect to a Slater-determ<strong>in</strong>ant basis consist<strong>in</strong>g of s<strong>in</strong>gle-<br />
particle harmonic oscillator states based on Cartesian coord<strong>in</strong>ates. This basis is<br />
also known as m-scheme basis. Consequently, we have to derive and implement<br />
the transformation from Jacobi to m-scheme matrix elements, which will <strong>in</strong>clude<br />
two harmonic oscillator brackets. It turns out that this is a non-trivial task, be-<br />
cause it is computational demand<strong>in</strong>g. Generally, we follow the strategy outl<strong>in</strong>ed <strong>in</strong><br />
[5] and precompute a certa<strong>in</strong> overlap coefficient to speed up the transformation<br />
code. Hav<strong>in</strong>g the m-scheme matrix elements we are <strong>in</strong> pr<strong>in</strong>ciple able to attack the<br />
eigenvalue problem of the Hamiltonian. But the storage of m-scheme matrix ele-<br />
ments becomes problematic even for modest model space sizes. Therefore, our<br />
strategy is to compute matrix elements with respect to states that carry a total<br />
coupled angular momentum J and isosp<strong>in</strong> T . These matrix elements are then<br />
decoupled to m-scheme matrix elements <strong>in</strong> the many-body calculation. With this<br />
strategy it is possible for the first time to calculate matrix elements of the N2LO<br />
<strong>three</strong>-<strong>nucleon</strong> <strong>in</strong>teraction up to a total <strong>three</strong>-particle harmonic oscillator energies<br />
J. Langhammer 3