SKF Reliability Systems - Library
SKF Reliability Systems - Library
SKF Reliability Systems - Library
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
PM Reviews at Sydney Water 42 Vol 23 No 3 AMMJ<br />
EXPECTATIONS FROM PM SCHEDULES<br />
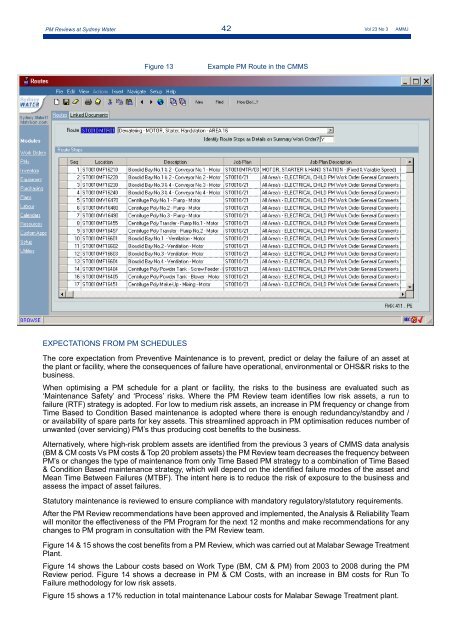
Figure 13 Example PM Route in the CMMS<br />
The core expectation from Preventive Maintenance is to prevent, predict or delay the failure of an asset at<br />
the plant or facility, where the consequences of failure have operational, environmental or OHS&R risks to the<br />
business.<br />
When optimising a PM schedule for a plant or facility, the risks to the business are evaluated such as<br />
‘Maintenance Safety’ and ‘Process’ risks. Where the PM Review team identifies low risk assets, a run to<br />
failure (RTF) strategy is adopted. For low to medium risk assets, an increase in PM frequency or change from<br />
Time Based to Condition Based maintenance is adopted where there is enough redundancy/standby and /<br />
or availability of spare parts for key assets. This streamlined approach in PM optimisation reduces number of<br />
unwanted (over servicing) PM’s thus producing cost benefits to the business.<br />
Alternatively, where high-risk problem assets are identified from the previous 3 years of CMMS data analysis<br />
(BM & CM costs Vs PM costs & Top 20 problem assets) the PM Review team decreases the frequency between<br />
PM’s or changes the type of maintenance from only Time Based PM strategy to a combination of Time Based<br />
& Condition Based maintenance strategy, which will depend on the identified failure modes of the asset and<br />
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF). The intent here is to reduce the risk of exposure to the business and<br />
assess the impact of asset failures.<br />
Statutory maintenance is reviewed to ensure compliance with mandatory regulatory/statutory requirements.<br />
After the PM Review recommendations have been approved and implemented, the Analysis & <strong>Reliability</strong> Team<br />
will monitor the effectiveness of the PM Program for the next 12 months and make recommendations for any<br />
changes to PM program in consultation with the PM Review team.<br />
Figure 14 & 15 shows the cost benefits from a PM Review, which was carried out at Malabar Sewage Treatment<br />
Plant.<br />
Figure 14 shows the Labour costs based on Work Type (BM, CM & PM) from 2003 to 2008 during the PM<br />
Review period. Figure 14 shows a decrease in PM & CM Costs, with an increase in BM costs for Run To<br />
Failure methodology for low risk assets.<br />
Figure 15 shows a 17% reduction in total maintenance Labour costs for Malabar Sewage Treatment plant.