An Introduction to Neutron Scattering - Spallation Neutron Source
An Introduction to Neutron Scattering - Spallation Neutron Source
An Introduction to Neutron Scattering - Spallation Neutron Source
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
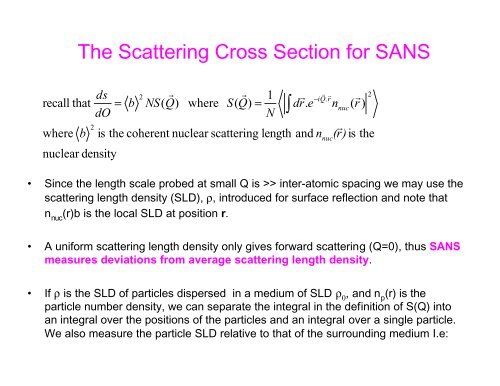
ecall that<br />
where<br />
The <strong>Scattering</strong> Cross Section for SANS<br />
b<br />
nuclear density<br />
2<br />
ds<br />
dO<br />
=<br />
b<br />
2<br />
NS(<br />
Q)<br />
r r 1<br />
r<br />
−iQ.<br />
r<br />
where<br />
r<br />
S(<br />
Q)<br />
=<br />
r<br />
dr.<br />
e<br />
is the coherent nuclear scattering length and n<br />
r<br />
( r)<br />
is<br />
• Since the length scale probed at small Q is >> inter-a<strong>to</strong>mic spacing we may use the<br />
scattering length density (SLD), ρ, introduced for surface reflection and note that<br />
n nuc (r)b is the local SLD at position r.<br />
• A uniform scattering length density only gives forward scattering (Q=0), thus SANS<br />
measures deviations from average scattering length density.<br />
• If ρ is the SLD of particles dispersed in a medium of SLD ρ 0 , and n p (r) is the<br />
particle number density, we can separate the integral in the definition of S(Q) in<strong>to</strong><br />
an integral over the positions of the particles and an integral over a single particle.<br />
We also measure the particle SLD relative <strong>to</strong> that of the surrounding medium I.e:<br />
N<br />
∫<br />
nuc<br />
n<br />
nuc<br />
r<br />
( r )<br />
2<br />
the