- Page 1 and 2:
y Roger Pynn Los Alamos National La
- Page 3 and 4:
Why do Neutron Scattering? • To d
- Page 5 and 6:
The Neutron has Both Particle-Like
- Page 7 and 8:
Thermal Neutrons, 8 keV X-Rays & Lo
- Page 9 and 10:
Brightness & Fluxes for Neutron & X
- Page 11 and 12:
Scattering by a Single (fixed) Nucl
- Page 13 and 14:
Coherent and Incoherent Scattering
- Page 15 and 16:
so or ie Coherent Elastic Scatterin
- Page 17 and 18:
Neutrons can also gain or lose ener
- Page 19 and 20:
Magnetic Scattering • The magneti
- Page 21 and 22:
Ene rgy Trans fe r (me V) 10000 100
- Page 23 and 24:
References • Introduction to the
- Page 25 and 26:
Overview 1. Essential messages from
- Page 27 and 28:
What Do We Need to Do a Basic Neutr
- Page 29 and 30:
About 1.5 Useful Neutrons Are Produ
- Page 31 and 32:
The ESRF* & ILL* With Grenoble & th
- Page 33 and 34:
Neutron Sources Provide Neutrons fo
- Page 35 and 36:
Proton Radiography 800-MeV Linear A
- Page 37 and 38:
Components of a Spallation Source A
- Page 39 and 40:
Simultaneously Using Neutrons With
- Page 41 and 42:
The Actual ToF Gain From Source Pul
- Page 43 and 44:
Why Isn’t There a Universal Neutr
- Page 45 and 46:
• Uncertainties in the neutron wa
- Page 47 and 48:
Typical Neutron Scattering Instrume
- Page 49 and 50:
Most Neutron Detectors Use 3 He •
- Page 51 and 52:
Rotating Choppers Are Used to Tailo
- Page 53 and 54:
3. Diffraction Next Lecture 1. Diff
- Page 55 and 56:
2. Diffraction This Lecture 1. Diff
- Page 57 and 58:
Neutron Diffraction • Neutron dif
- Page 59 and 60:
For Periodic Arrays of Nuclei, Cohe
- Page 61 and 62:
We would be better off if diffracti
- Page 63 and 64:
Powder - A Polycrystalline Mass All
- Page 65 and 66:
Measuring Neutron Diffraction Patte
- Page 67 and 68:
Time-of-Flight Powder Diffraction U
- Page 69 and 70:
There’s more than meets the eye i
- Page 71 and 72:
How good is this function? Protein
- Page 73 and 74:
High-resolution Neutron Powder Diff
- Page 75 and 76:
Texture Measurement by Diffraction
- Page 77 and 78:
Definitions of Stress and Strain
- Page 79 and 80:
Why use Metal Matrix Composites ? F
- Page 81 and 82:
Neutron Diffraction Measures Mean R
- Page 83 and 84:
Deformation Mechanism in U/Nb Alloy
- Page 85 and 86:
Obtaining the Pair Distribution Fun
- Page 87 and 88:
Effect of Doping on the Octahedra
- Page 89 and 90:
Surface Reflection Is Very Differen
- Page 91 and 92:
What Is the Neutron Wavevector Insi
- Page 93 and 94:
Only Those Thermal or Cold Neutrons
- Page 95 and 96:
What do the Amplitudes a R and a T
- Page 97 and 98:
Fresnel’s Law for a Thin Film •
- Page 99 and 100:
Reflection by a Graded Interface io
- Page 101 and 102:
Direct Inversion of Reflectivity Da
- Page 103 and 104:
4 R*Q z 10 -7 10 -8 10 -9 1.3% PEG
- Page 105 and 106:
Polarized Neutron Reflectometry (PN
- Page 107 and 108:
Reflection from Rough Surfaces z z
- Page 109 and 110:
fi fi fi Q =kf -ki Qx-Qz Transforma
- Page 111 and 112:
Observation of Hexagonal Packing of
- Page 113 and 114:
This Lecture 5. Small Angle Neutron
- Page 115 and 116:
Two Views of the Components of a Ty
- Page 117 and 118:
Where Does SANS Fit As a Structural
- Page 119 and 120:
Instrumental Resolution for SANS Tr
- Page 121 and 122:
SANS Measures Particle Shapes and I
- Page 123 and 124:
Examples of Spherically-Averaged Fo
- Page 125 and 126:
Correlations Can Be Measured in Con
- Page 127 and 128: Radius of Gyration Is the Particle
- Page 129 and 130: Contrast & Contrast Matching Water
- Page 131 and 132: Verification of of the Gaussian Coi
- Page 133 and 134: Porod Scattering function. n correl
- Page 135 and 136: ln(I) Typical Intensity Plot for SA
- Page 137 and 138: References • Viewgraphs describin
- Page 139 and 140: We Have Seen How Neutron Scattering
- Page 141 and 142: The Elastic & Inelastic Scattering
- Page 143 and 144: Examples of S(Q,ω) and S s(Q,ω)
- Page 145 and 146: Inelastic Magnetic Scattering of Ne
- Page 147 and 148: Measured Inelastic Neutron Scatteri
- Page 149 and 150: Atomic Motions for Longitudinal & T
- Page 151 and 152: Phonons - the Classical Use for Ine
- Page 153 and 154: The Accessible Energy and Wavevecto
- Page 155 and 156: What Use Have Phonon Measurements B
- Page 157 and 158: Time-of-flight Methods Can Give Com
- Page 159 and 160: Neutron Spin Echo By Roger Pynn* Lo
- Page 161 and 162: • Uncertainties in the neutron wa
- Page 163 and 164: The Underlying Physics of Neutron S
- Page 165 and 166: How does a Neutron Spin Behave when
- Page 167 and 168: The Principles of NSE are Very Simp
- Page 169 and 170: For Quasi-elastic Scattering, the E
- Page 171 and 172: Neutron counts ( per 50 sec) Neutro
- Page 173 and 174: Field-Integral Inhomogeneities caus
- Page 175 and 176: Neutron Spin Echo study of Deformat
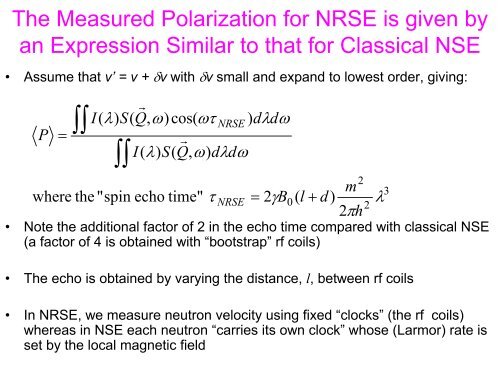
- Page 177: Neutron Spin Phases NRSE spectromet
- Page 181 and 182: Measuring Line Shapes for Inelastic
- Page 183 and 184: “Phonon Focusing” • For a sin
- Page 185 and 186: An NRSE Triple Axis Spectrometer at
- Page 187 and 188: “Tilted” Fields for Diffraction
- Page 189 and 190: Spin Echo SANS using Magnetic Films
- Page 191: Conclusion: NSE Provides a Way to S