CFHT operating manual - Homepage Usask
CFHT operating manual - Homepage Usask
CFHT operating manual - Homepage Usask
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
ESPaDOnS: performances of Fresnel rhomb retarders http://webast.ast.obs-mip.fr/magnetisme/espadons_new/rhombs.html<br />
ESPaDOnS<br />
performances of Fresnel rhomb retarders<br />
Rhomb characteristics<br />
Given the large wavelength domain of ESPaDOnS, the first natural idea is to use superachromatic retarders designed along<br />
Serkowsky’s ideas, like those manufactured by Halle. However, previous experience with them demonstrated that they generate<br />
large amplitude fringing in the intensity and polarisation spectra and thus drastically reduce the polarisation accuracy of any<br />
potential measurements obtained with them. We therefore decided to use Fresnel rhombs, that were proven to be much more<br />
achromatic and producing almost no fringing patterns in high resolution spectra.<br />
A bunch of 24 single bk7 rhombs (with birefringence smaller than 0.2nm/cm) was ordered and constructed along detailed<br />
specifications, to construct 8 quarter-wave (single) rhombs and 8 half-wave (double) rhombs, with different thicknesses of MgF2<br />
coating to study the effect on the rhomb retardance. The rhombs are mounted in a specific barrel filled with helium (to avoid<br />
oxydation of the totally reflecting surfaces) and sealed with a soft joint. A dedicated and fully automated optical bench was also<br />
designed and constructed to measure the rhombs retardance with an accuracy of 0.1deg. The best rhombs were selected for the<br />
polarimeter modules of ESPaDOnS and NARVAL (the copy of ESPaDOnS in construction for the 2m Bernard Lyot telescope<br />
atop Pic du Midi).<br />
Retardance accuracy<br />
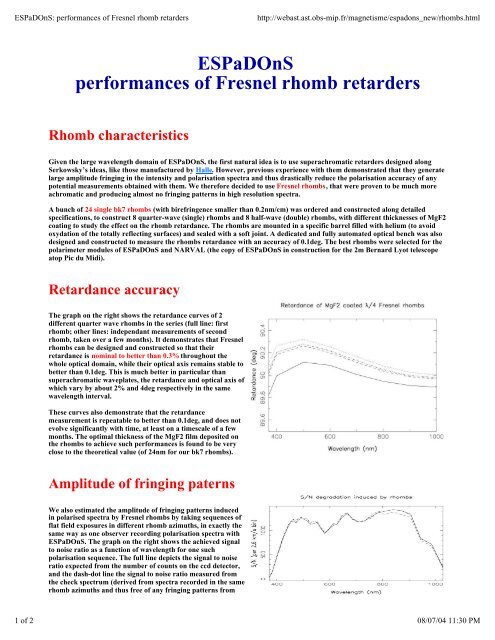
The graph on the right shows the retardance curves of 2<br />
different quarter wave rhombs in the series (full line: first<br />
rhomb; other lines: independant measurements of second<br />
rhomb, taken over a few months). It demonstrates that Fresnel<br />
rhombs can be designed and constructed so that their<br />
retardance is nominal to better than 0.3% throughout the<br />
whole optical domain, while their optical axis remains stable to<br />
better than 0.1deg. This is much better in particular than<br />
superachromatic waveplates, the retardance and optical axis of<br />
which vary by about 2% and 4deg respectively in the same<br />
wavelength interval.<br />
These curves also demonstrate that the retardance<br />
measurement is repeatable to better than 0.1deg, and does not<br />
evolve significantly with time, at least on a timescale of a few<br />
months. The optimal thickness of the MgF2 film deposited on<br />
the rhombs to achieve such performances is found to be very<br />
close to the theoretical value (of 24nm for our bk7 rhombs).<br />
Amplitude of fringing paterns<br />
We also estimated the amplitude of fringing patterns induced<br />
in polarised spectra by Fresnel rhombs by taking sequences of<br />
flat field exposures in different rhomb azimuths, in exactly the<br />
same way as one observer recording polarisation spectra with<br />
ESPaDOnS. The graph on the right shows the achieved signal<br />
to noise ratio as a function of wavelength for one such<br />
polarisation sequence. The full line depicts the signal to noise<br />
ratio expected from the number of counts on the ccd detector,<br />
and the dash-dot line the signal to noise ratio measured from<br />
the check spectrum (derived from spectra recorded in the same<br />
rhomb azimuths and thus free of any fringing patterns from<br />
1 of 2 08/07/04 11:30 PM