Valeurs seuils pour le rapport coût-efficacité en soins de santé - KCE
Valeurs seuils pour le rapport coût-efficacité en soins de santé - KCE
Valeurs seuils pour le rapport coût-efficacité en soins de santé - KCE
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>KCE</strong> reports 100 ICER Thresholds 11<br />
The ICER of an interv<strong>en</strong>tion could be compared to a certain ICER threshold value or to<br />
ICERs of other interv<strong>en</strong>tions for other conditions. The lower the ICER, the more<br />
additional health can be obtained with the same additional value of resource inputs, and<br />
thus the more cost-effective an interv<strong>en</strong>tion is consi<strong>de</strong>red. 2-4<br />
Key points<br />
• The increm<strong>en</strong>tal cost-effectiv<strong>en</strong>ess ratio (ICER) is the ratio of the<br />
estimated differ<strong>en</strong>ce betwe<strong>en</strong> the costs of two interv<strong>en</strong>tions and the<br />
estimated differ<strong>en</strong>ce betwe<strong>en</strong> the outcomes of these two interv<strong>en</strong>tions.<br />
• The ICER repres<strong>en</strong>ts the estimated additional cost per extra unit of<br />
health b<strong>en</strong>efit g<strong>en</strong>erated by an interv<strong>en</strong>tion compared with an<br />
appropriate comparator. The appropriate comparator is the most costeffective<br />
alternative for the same health condition.<br />
• The ICER int<strong>en</strong>ds to support informed <strong>de</strong>cision making about<br />
interv<strong>en</strong>tions that are both more costly and more effective than their<br />
comparator (or inversely <strong>le</strong>ss effective but cheaper).<br />
2.3 THE COST-EFFECTIVENESS PLANE<br />
The results of a full economic evaluation can be repres<strong>en</strong>ted graphically on a costeffectiv<strong>en</strong>ess<br />
plane (Figure 2). 2<br />
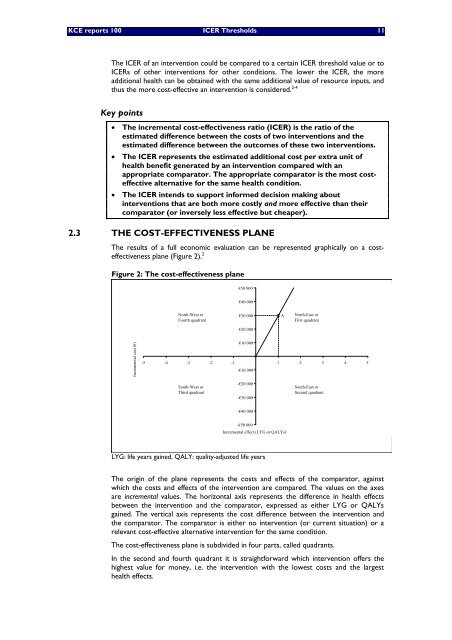
Figure 2: The cost-effectiv<strong>en</strong>ess plane<br />
Increm<strong>en</strong>tal cost (€)<br />
North-West or<br />
Fourth quadrant<br />
€50 000<br />
€40 000<br />
€30 000<br />
€20 000<br />
€10 000<br />
-5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5<br />
South-West or<br />
Third quadrant<br />
-€10 000<br />
-€20 000<br />
-€30 000<br />
-€40 000<br />
-€50 000<br />
Increm<strong>en</strong>tal effect (LYG or QALYs)<br />
LYG: life years gained, QALY: quality-adjusted life years<br />
A<br />
North-East or<br />
First quadrant<br />
South-East or<br />
Second quadrant<br />
The origin of the plane repres<strong>en</strong>ts the costs and effects of the comparator, against<br />
which the costs and effects of the interv<strong>en</strong>tion are compared. The values on the axes<br />
are increm<strong>en</strong>tal values. The horizontal axis repres<strong>en</strong>ts the differ<strong>en</strong>ce in health effects<br />
betwe<strong>en</strong> the interv<strong>en</strong>tion and the comparator, expressed as either LYG or QALYs<br />
gained. The vertical axis repres<strong>en</strong>ts the cost differ<strong>en</strong>ce betwe<strong>en</strong> the interv<strong>en</strong>tion and<br />
the comparator. The comparator is either no interv<strong>en</strong>tion (or curr<strong>en</strong>t situation) or a<br />
re<strong>le</strong>vant cost-effective alternative interv<strong>en</strong>tion for the same condition.<br />
The cost-effectiv<strong>en</strong>ess plane is subdivi<strong>de</strong>d in four parts, cal<strong>le</strong>d quadrants.<br />
In the second and fourth quadrant it is straightforward which interv<strong>en</strong>tion offers the<br />
highest value for money, i.e. the interv<strong>en</strong>tion with the lowest costs and the largest<br />
health effects.