influence of oxalic acid on the catalytic s
influence of oxalic acid on the catalytic s
influence of oxalic acid on the catalytic s
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
140<br />
Based <strong>on</strong> <strong>the</strong> measurement results, <strong>the</strong> kinetic<br />
law parameters for <strong>the</strong> processes studied were<br />
determined. Since <strong>the</strong> rate <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> Mn(II)-catalysed<br />
S(IV) oxidati<strong>on</strong> is independent <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> oxygen<br />
where kobs is <strong>the</strong> observed rate c<strong>on</strong>stant, and n is<br />
<strong>the</strong> reacti<strong>on</strong> order with respect to S(IV)<br />
c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>. The observed rate c<strong>on</strong>stant kobs is<br />
a functi<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> Mn(II) and <str<strong>on</strong>g>oxalic</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>acid</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
[H2C2O4]<br />
mol/dm 3<br />
Initial pH = 3.5<br />
d[<br />
S(IV) ]<br />
r ]<br />
dt<br />
c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong> (Huss et al., 1982; C<strong>on</strong>nick and<br />
Zhang, 1996), <strong>the</strong> reacti<strong>on</strong> rate has been<br />
described by <strong>the</strong> equati<strong>on</strong>:<br />
n<br />
= − = kobs<br />
[ S(IV)<br />
(1)<br />
c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s as well as <strong>the</strong> initial pH <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>the</strong><br />
soluti<strong>on</strong>. The reacti<strong>on</strong> orders and <strong>the</strong> observed<br />
rate c<strong>on</strong>stants determined by <strong>the</strong> standard<br />
integral technique are listed in Tables 1 - 2.<br />
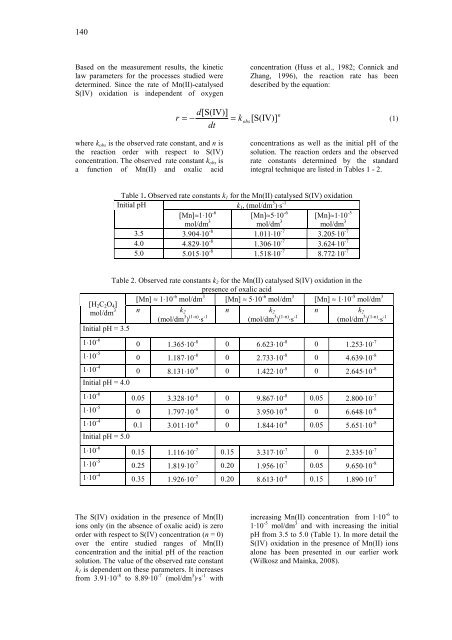
Table 1. Observed rate c<strong>on</strong>stants k1 for <strong>the</strong> Mn(II) catalysed S(IV) oxidati<strong>on</strong><br />
k1, (mol/dm 3 )⋅s -1<br />
Initial pH<br />
[Mn]≈1⋅10 -6<br />
mol/dm 3<br />
[Mn]≈5⋅10 -6<br />
mol/dm 3<br />
[Mn]≈1⋅10 -5<br />
mol/dm 3<br />
3.5 3.904⋅10 -8 1.011⋅10 -7 3.205⋅10 -7<br />
4.0 4.829⋅10 -8 1.306⋅10 -7 3.624⋅10 -7<br />
5.0 5.015⋅10 -8 1.518⋅10 -7 8.772⋅10 -7<br />
Table 2. Observed rate c<strong>on</strong>stants k2 for <strong>the</strong> Mn(II) catalysed S(IV) oxidati<strong>on</strong> in <strong>the</strong><br />
presence <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>oxalic</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>acid</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
[Mn] ≈ 1⋅10 -6 mol/dm 3 [Mn] ≈ 5⋅10 -6 mol/dm 3 [Mn] ≈ 1⋅10 -5 mol/dm 3<br />
n k2<br />
(mol/dm 3 ) (1-n) ⋅s -1<br />
n k2<br />
(mol/dm 3 ) (1-n) ⋅s -1<br />
n k2<br />
(mol/dm 3 ) (1-n) ⋅s -1<br />
1⋅10 -6 0 1.365⋅10 -8 0 6.623⋅10 -8 0 1.253⋅10 -7<br />
1⋅10 -5<br />
1⋅10 -4<br />
Initial pH = 4.0<br />
0 1.187⋅10 -8 0 2.733⋅10 -8 0 4.639⋅10 -8<br />
0 8.131⋅10 -9 0 1.422⋅10 -8 0 2.645⋅10 -8<br />
1⋅10 -6 0.05 3.328⋅10 -8 0 9.867⋅10 -8 0.05 2.800⋅10 -7<br />
1⋅10 -5<br />
1⋅10 -4<br />
Initial pH = 5.0<br />
0 1.797⋅10 -8 0 3.950⋅10 -8 0 6.648⋅10 -8<br />
0.1 3.011⋅10 -8 0 1.844⋅10 -8 0.05 5.651⋅10 -8<br />
1⋅10 -6 0.15 1.116⋅10 -7 0.15 3.317⋅10 -7 0 2.335⋅10 -7<br />
1⋅10 -5<br />
1⋅10 -4<br />
0.25 1.819⋅10 -7 0.20 1.956⋅10 -7 0.05 9.650⋅10 -8<br />
0.35 1.926⋅10 -7 0.20 8.613⋅10 -8 0.15 1.890⋅10 -7<br />
The S(IV) oxidati<strong>on</strong> in <strong>the</strong> presence <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> Mn(II)<br />
i<strong>on</strong>s <strong>on</strong>ly (in <strong>the</strong> absence <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>oxalic</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>acid</str<strong>on</strong>g>) is zero<br />
order with respect to S(IV) c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong> (n = 0)<br />
over <strong>the</strong> entire studied ranges <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> Mn(II)<br />
c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong> and <strong>the</strong> initial pH <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>the</strong> reacti<strong>on</strong><br />
soluti<strong>on</strong>. The value <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>the</strong> observed rate c<strong>on</strong>stant<br />
k1 is dependent <strong>on</strong> <strong>the</strong>se parameters. It increases<br />
from 3.91·10 -8 to 8.89·10 -7 (mol/dm 3 )·s -1 with<br />
increasing Mn(II) c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong> from 1·10 -6 to<br />
1·10 -5 mol/dm 3 and with increasing <strong>the</strong> initial<br />
pH from 3.5 to 5.0 (Table 1). In more detail <strong>the</strong><br />
S(IV) oxidati<strong>on</strong> in <strong>the</strong> presence <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> Mn(II) i<strong>on</strong>s<br />
al<strong>on</strong>e has been presented in our earlier work<br />
(Wilkosz and Mainka, 2008).