- Page 1:
Nonparametric Bayesian Discrete Lat
- Page 4 and 5:
Matrizen mit unendlich vielen Spalt
- Page 7 and 8:
Contents Zusammenfassung iii Abstra
- Page 9:
List of Algorithms 1 Gibbs sampling
- Page 13 and 14:
Notation Matrices are capitalized a
- Page 15:
Symbol Meaning IBP Z binary latent
- Page 18 and 19:
1 Introduction belief in the prior.
- Page 20 and 21:
2 Nonparametric Bayesian Analysis b
- Page 22 and 23:
2 Nonparametric Bayesian Analysis s
- Page 25 and 26:
3 Dirichlet Process Mixture Models
- Page 27 and 28:
3.1 The Dirichlet Process the perfo
- Page 29 and 30:
α G o G θi x i N 3.1 The Dirichle
- Page 31 and 32:
15 10 5 −0.5 0 0.5 2 1 G 0 0 −0
- Page 33 and 34:
increment process with the correspo
- Page 35 and 36:
α G o π k c i θk x i 8 N 3.1 The
- Page 37 and 38:
3.1 The Dirichlet Process Eq. (3.21
- Page 39 and 40:
number of components, K number of c
- Page 41 and 42:
3.2 MCMC Inference in Dirichlet Pro
- Page 43 and 44:
and Bush and MacEachern (1996). 3.2
- Page 45 and 46:
3.2.2 Algorithms for non-Conjugate
- Page 47 and 48:
3.2 MCMC Inference in Dirichlet Pro
- Page 49 and 50:
3.2 MCMC Inference in Dirichlet Pro
- Page 51 and 52:
3.2 MCMC Inference in Dirichlet Pro
- Page 53 and 54:
3.2 MCMC Inference in Dirichlet Pro
- Page 55 and 56:
∗ π ∗ π s 3.2 MCMC Inference
- Page 57 and 58:
model can be written in the form of
- Page 59 and 60:
−1 µ y Σy Σy D ξ normal R 3.3
- Page 61 and 62:
the log likelihood term is: where a
- Page 63 and 64:
3.3 Empirical Study on the Choice o
- Page 65 and 66:
autocovariance coefficient 1 0.8 0.
- Page 67 and 68:
# of data points # of data points 5
- Page 69 and 70:
3.4 Dirichlet Process Mixtures of F
- Page 71 and 72: µ y Σy ξ R 0 ν w normal µ −1
- Page 73 and 74: ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 3.4 Dirichlet Proce
- Page 75 and 76: 3.4 Dirichlet Process Mixtures of F
- Page 77 and 78: # of components # of components # o
- Page 79 and 80: ch 2 ch 3 ch 1 ch 2 ch 3 ch 4 3.4 D
- Page 81: 3.5 Discussion 3.5 Discussion In th
- Page 84 and 85: 4 Indian Buffet Process Models matr
- Page 86 and 87: 4 Indian Buffet Process Models In t
- Page 88 and 89: 4 Indian Buffet Process Models α z
- Page 90 and 91: 4 Indian Buffet Process Models α
- Page 92 and 93: 4 Indian Buffet Process Models The
- Page 94 and 95: 4 Indian Buffet Process Models colu
- Page 96 and 97: 4 Indian Buffet Process Models Pois
- Page 98 and 99: 4 Indian Buffet Process Models z α
- Page 100 and 101: 4 Indian Buffet Process Models For
- Page 102 and 103: 4 Indian Buffet Process Models ciat
- Page 104 and 105: 4 Indian Buffet Process Models rati
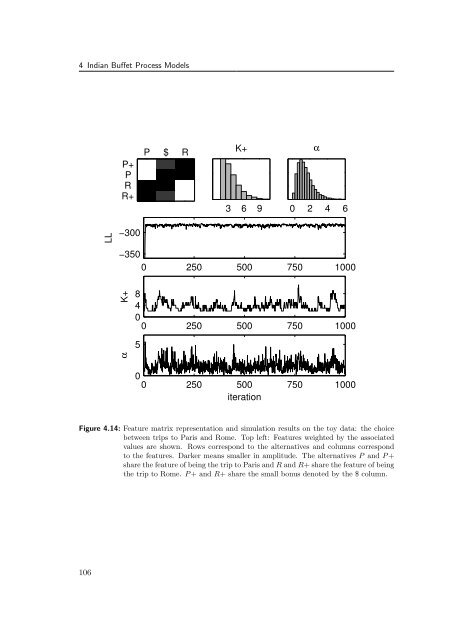
- Page 106 and 107: 4 Indian Buffet Process Models repr
- Page 108 and 109: 4 Indian Buffet Process Models samp
- Page 110 and 111: 4 Indian Buffet Process Models feat
- Page 112 and 113: 4 Indian Buffet Process Models Algo
- Page 114 and 115: 4 Indian Buffet Process Models mixi
- Page 116 and 117: 4 Indian Buffet Process Models Figu
- Page 118 and 119: 4 Indian Buffet Process Models pres
- Page 120 and 121: 4 Indian Buffet Process Models ε
- Page 124 and 125: 4 Indian Buffet Process Models P+ P
- Page 126 and 127: 4 Indian Buffet Process Models tEBA
- Page 128 and 129: 4 Indian Buffet Process Models dist
- Page 130 and 131: 5 Conclusions has been defined as a
- Page 132 and 133: A Details of Derivations for the St
- Page 135 and 136: B Mathematical Appendix B.1 Dirichl
- Page 137 and 138: p3 α 1 0.5 0 0 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1
- Page 139 and 140: Construction of A Process B.4 Equal
- Page 141 and 142: Bibliography D. Aldous. Exchangeabi
- Page 143 and 144: Bibliography T. S. Ferguson. Prior
- Page 145 and 146: Bibliography L. F. James and J. W.
- Page 147 and 148: Bibliography R. M. Neal. Probabilis
- Page 149 and 150: Bibliography Y. W. Teh, M. I. Jorda