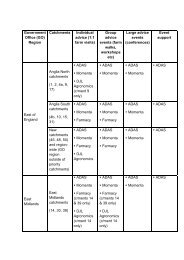
Guidelines for Metals and Metalloids in Ambient ... - ARCHIVE: Defra
Guidelines for Metals and Metalloids in Ambient ... - ARCHIVE: Defra
Guidelines for Metals and Metalloids in Ambient ... - ARCHIVE: Defra
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Expert Panel on Air Quality St<strong>and</strong>ards<br />
(from coal combustion) was soluble <strong>and</strong> associated primarily with<br />
sulphate. Thus, nickel emissions to atmosphere from coal <strong>and</strong> oil<br />
combustion are likely to be composed ma<strong>in</strong>ly of (soluble) nickel<br />
sulphate, with smaller amounts of nickel oxide <strong>and</strong> nickel comb<strong>in</strong>ed<br />
with other metals <strong>in</strong> complex oxides. Alterations <strong>in</strong> the chemical <strong>for</strong>ms,<br />
follow<strong>in</strong>g distribution <strong>in</strong> the atmosphere, have not been <strong>in</strong>vestigated.<br />
116. The distribution of nickel among suspended particulate matter <strong>in</strong> air<br />
will determ<strong>in</strong>e the fraction that is <strong>in</strong>halable. Data on the size<br />
distribution of nickel particles are limited. Lee <strong>and</strong> von Lehmden<br />
(1973) reported mass median diameters of nickel particles <strong>in</strong> urban air<br />
<strong>in</strong> the range of 0.83-1.67 µm, 28-55% of the particulate matter be<strong>in</strong>g<br />