Boundary-layer height detection with a ceilometer at a coastal ... - Orbit
Boundary-layer height detection with a ceilometer at a coastal ... - Orbit
Boundary-layer height detection with a ceilometer at a coastal ... - Orbit
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
1400<br />
β profile 01/05/2010 15:20<br />
1400<br />
δβ smooth<br />
/δz profile 01/05/2010 15:20<br />
1200<br />
1200<br />
1000<br />
1000<br />
Height [m]<br />
800<br />
600<br />
Height [m]<br />
800<br />
600<br />
400<br />
400<br />
200<br />
200<br />
0<br />
−50 0 50 100 150 200<br />
Backsc<strong>at</strong>ter [1/(10 8 *srad*m)]<br />
0<br />
−1 −0.5 0 0.5<br />
Backsc<strong>at</strong>ter gradient [1/(10 8 *srad*m 2 )]<br />
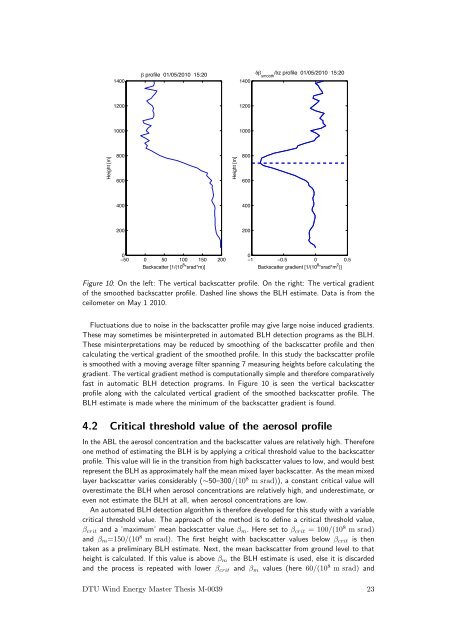
Figure 10: On the left: The vertical backsc<strong>at</strong>ter profile. On the right: The vertical gradient<br />
of the smoothed backsc<strong>at</strong>ter profile. Dashed line shows the BLH estim<strong>at</strong>e. D<strong>at</strong>a is from the<br />
<strong>ceilometer</strong> on May 1 2010.<br />
Fluctu<strong>at</strong>ions due to noise in the backsc<strong>at</strong>ter profile may give large noise induced gradients.<br />
These may sometimes be misinterpreted in autom<strong>at</strong>ed BLH <strong>detection</strong> programs as the BLH.<br />
These misinterpret<strong>at</strong>ions may be reduced by smoothing of the backsc<strong>at</strong>ter profile and then<br />
calcul<strong>at</strong>ing the vertical gradient of the smoothed profile. In this study the backsc<strong>at</strong>ter profile<br />
is smoothed <strong>with</strong> a moving average filter spanning 7 measuring <strong>height</strong>s before calcul<strong>at</strong>ing the<br />
gradient. The vertical gradient method is comput<strong>at</strong>ionally simple and therefore compar<strong>at</strong>ively<br />
fast in autom<strong>at</strong>ic BLH <strong>detection</strong> programs. In Figure 10 is seen the vertical backsc<strong>at</strong>ter<br />
profile along <strong>with</strong> the calcul<strong>at</strong>ed vertical gradient of the smoothed backsc<strong>at</strong>ter profile. The<br />
BLH estim<strong>at</strong>e is made where the minimum of the backsc<strong>at</strong>ter gradient is found.<br />
4.2 Critical threshold value of the aerosol profile<br />
In the ABL the aerosol concentr<strong>at</strong>ion and the backsc<strong>at</strong>ter values are rel<strong>at</strong>ively high. Therefore<br />
one method of estim<strong>at</strong>ing the BLH is by applying a critical threshold value to the backsc<strong>at</strong>ter<br />
profile. This value will lie in the transition from high backsc<strong>at</strong>ter values to low, and would best<br />
represent the BLH as approxim<strong>at</strong>ely half the mean mixed <strong>layer</strong> backsc<strong>at</strong>ter. As the mean mixed<br />
<strong>layer</strong> backsc<strong>at</strong>ter varies considerably (∼50–300/(10 8 m srad)), a constant critical value will<br />
overestim<strong>at</strong>e the BLH when aerosol concentr<strong>at</strong>ions are rel<strong>at</strong>ively high, and underestim<strong>at</strong>e, or<br />
even not estim<strong>at</strong>e the BLH <strong>at</strong> all, when aerosol concentr<strong>at</strong>ions are low.<br />
An autom<strong>at</strong>ed BLH <strong>detection</strong> algorithm is therefore developed for this study <strong>with</strong> a variable<br />
critical threshold value. The approach of the method is to define a critical threshold value,<br />
β crit and a ’maximum’ mean backsc<strong>at</strong>ter value β m . Here set to β crit = 100/(10 8 m srad)<br />
and β m =150/(10 8 m srad). The first <strong>height</strong> <strong>with</strong> backsc<strong>at</strong>ter values below β crit is then<br />
taken as a preliminary BLH estim<strong>at</strong>e. Next, the mean backsc<strong>at</strong>ter from ground level to th<strong>at</strong><br />
<strong>height</strong> is calcul<strong>at</strong>ed. If this value is above β m the BLH estim<strong>at</strong>e is used, else it is discarded<br />
and the process is repe<strong>at</strong>ed <strong>with</strong> lower β crit and β m values (here 60/(10 8 m srad) and<br />
DTU Wind Energy Master Thesis M-0039 23