Click to download Ethernet Basics manual - Grant Industrial Controls
Click to download Ethernet Basics manual - Grant Industrial Controls
Click to download Ethernet Basics manual - Grant Industrial Controls
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
TCP/IP 38<br />
The second part of the answer is a software aspect: a universal communication service has<br />
<strong>to</strong> be active on every host. Although many software pro<strong>to</strong>cols are adapted for internet works,<br />
only one suite is really considered and that is used most for internet works. This suite is called<br />
TCP/IP suite.<br />
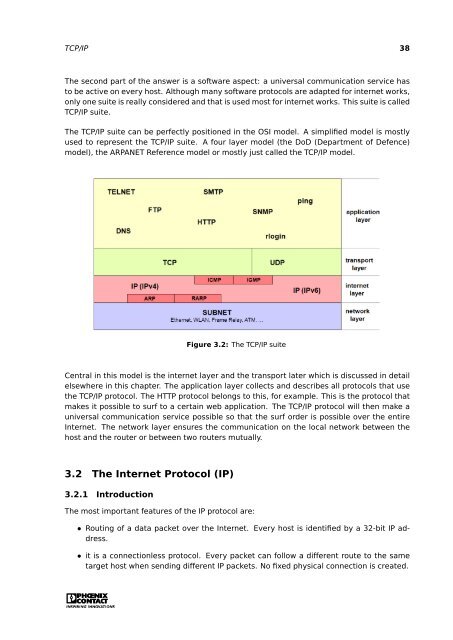
The TCP/IP suite can be perfectly positioned in the OSI model. A simplified model is mostly<br />
used <strong>to</strong> represent the TCP/IP suite. A four layer model (the DoD (Department of Defence)<br />
model), the ARPANET Reference model or mostly just called the TCP/IP model.<br />
Figure 3.2: The TCP/IP suite<br />
Central in this model is the internet layer and the transport later which is discussed in detail<br />
elsewhere in this chapter. The application layer collects and describes all pro<strong>to</strong>cols that use<br />
the TCP/IP pro<strong>to</strong>col. The HTTP pro<strong>to</strong>col belongs <strong>to</strong> this, for example. This is the pro<strong>to</strong>col that<br />
makes it possible <strong>to</strong> surf <strong>to</strong> a certain web application. The TCP/IP pro<strong>to</strong>col will then make a<br />
universal communication service possible so that the surf order is possible over the entire<br />
Internet. The network layer ensures the communication on the local network between the<br />
host and the router or between two routers mutually.<br />
3.2 The Internet Pro<strong>to</strong>col (IP)<br />
3.2.1 Introduction<br />
The most important features of the IP pro<strong>to</strong>col are:<br />
• Routing of a data packet over the Internet. Every host is identified by a 32-bit IP address.<br />
• it is a connectionless pro<strong>to</strong>col. Every packet can follow a different route <strong>to</strong> the same<br />
target host when sending different IP packets. No fixed physical connection is created.