Ferromagnetic (Ga,Mn)As Layers and ... - OPUS Würzburg
Ferromagnetic (Ga,Mn)As Layers and ... - OPUS Würzburg
Ferromagnetic (Ga,Mn)As Layers and ... - OPUS Würzburg
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
3.5. X-Ray Diffraction 35<br />
1 0 7<br />
1 0 6<br />
G a A s<br />
1 0 5<br />
(G a ,M n )A s<br />
In te n s ity [a .u .]<br />
1 0 4<br />
1 0 3<br />
1 0 2<br />
1 0 1<br />
1 0 0<br />
1 0 -1<br />
3 2 .6 3 2 .8 3 3 .0 3 3 .2 3 3 .4<br />
O m e g a [d e g .]<br />
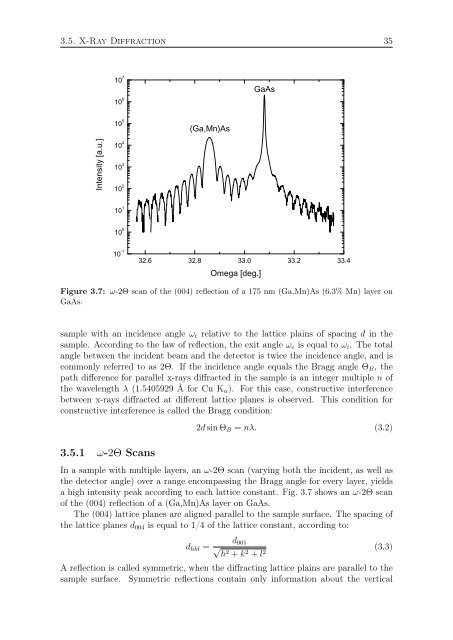
Figure 3.7: ω-2Θ scan of the (004) reflection of a 175 nm (<strong>Ga</strong>,<strong>Mn</strong>)<strong>As</strong> (6.3% <strong>Mn</strong>) layer on<br />
<strong>Ga</strong><strong>As</strong>.<br />
sample with an incidence angle ω i relative to the lattice plains of spacing d in the<br />
sample. According to the law of reflection, the exit angle ω e is equal to ω i . The total<br />
angle between the incident beam <strong>and</strong> the detector is twice the incidence angle, <strong>and</strong> is<br />
commonly referred to as 2Θ. If the incidence angle equals the Bragg angle Θ B , the<br />
path difference for parallel x-rays diffracted in the sample is an integer multiple n of<br />
the wavelength λ (1.5405929 Å for Cu K α ). For this case, constructive interference<br />
between x-rays diffracted at different lattice planes is observed. This condition for<br />
constructive interference is called the Bragg condition:<br />
3.5.1 ω-2Θ Scans<br />
2d sin Θ B = nλ. (3.2)<br />
In a sample with multiple layers, an ω-2Θ scan (varying both the incident, as well as<br />
the detector angle) over a range encompassing the Bragg angle for every layer, yields<br />
a high intensity peak according to each lattice constant. Fig. 3.7 shows an ω-2Θ scan<br />
of the (004) reflection of a (<strong>Ga</strong>,<strong>Mn</strong>)<strong>As</strong> layer on <strong>Ga</strong><strong>As</strong>.<br />
The (004) lattice planes are aligned parallel to the sample surface. The spacing of<br />
the lattice planes d 004 is equal to 1/4 of the lattice constant, according to:<br />
d hkl =<br />
d 001<br />
√<br />
h2 + k 2 + l 2 (3.3)<br />
A reflection is called symmetric, when the diffracting lattice plains are parallel to the<br />
sample surface. Symmetric reflections contain only information about the vertical