DRUG-INDUCED LEUKOPENIA
DRUG-INDUCED LEUKOPENIA
DRUG-INDUCED LEUKOPENIA
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
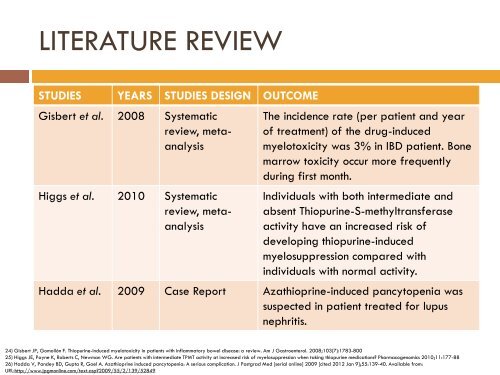
LITERATURE REVIEW<br />
STUDIES<br />
YEARS STUDIES DESIGN OUTCOME<br />
Gisbert et al. 2008 Systematic<br />
review, metaanalysis<br />
Higgs et al. 2010 Systematic<br />
review, metaanalysis<br />
The incidence rate (per patient and year<br />
of treatment) of the drug-induced<br />
myelotoxicity was 3% in IBD patient. Bone<br />
marrow toxicity occur more frequently<br />
during first month.<br />
Individuals with both intermediate and<br />
absent Thiopurine-S-methyltransferase<br />
activity have an increased risk of<br />
developing thiopurine-induced<br />
myelosuppression compared with<br />
individuals with normal activity.<br />
Hadda et al. 2009 Case Report Azathioprine-induced pancytopenia was<br />
suspected in patient treated for lupus<br />
nephritis.<br />
24) Gisbert JP, Gomollón F. Thiopurine-induced myelotoxicity in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008;103(7):1783-800<br />
25) Higgs JE, Payne K, Roberts C, Newman WG. Are patients with intermediate TPMT activity at increased risk of myelosuppression when taking thiopurine medications? Pharmacogenomics 2010;11:177-88<br />
26) Hadda V, Pandey BD, Gupta R, Goel A. Azathioprine induced pancytopenia: A serious complication. J Postgrad Med [serial online] 2009 [cited 2012 Jan 9];55:139-40. Available from:<br />
URL:http://www.jpgmonline.com/text.asp?2009/55/2/139/52849