Optical Coatings
Optical Coatings
Optical Coatings
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
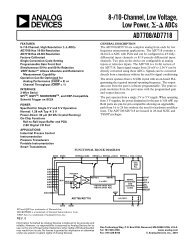
Paraxial Formulas<br />
SIGN CONVENTIONS<br />
The validity of the paraxial lens formulas is dependent on adherence to the following sign conventions:<br />
For lenses: (refer to figure 1.1)<br />
s is 1 for object to left of H<br />
(the first principal point)<br />
s is 5 for object to right of H<br />
s″ is 1 for image to right of H″<br />
(the second principal point)<br />
s″ is 5 for image to left of H″<br />
m is 1 for an inverted image<br />
m is 5 for an upright image<br />
For mirrors:<br />
When using the thin-lens approximation, simply refer to the left and right of the lens.<br />
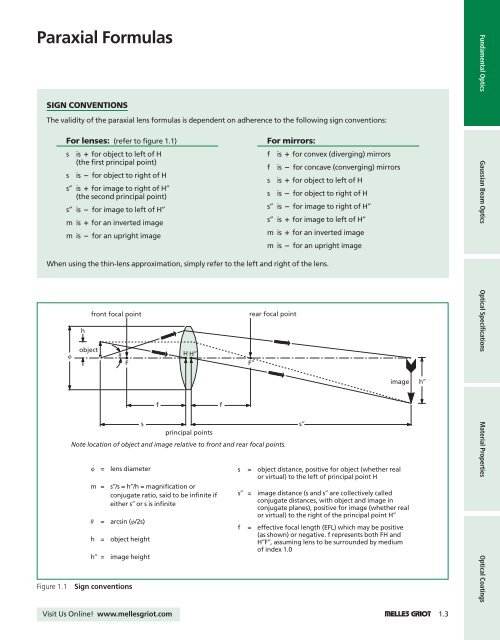
Figure 1.1<br />
h<br />
front focal point<br />
f object v<br />
H H″<br />
F<br />
s<br />
f<br />
principal points<br />
f<br />
f is 1 for convex (diverging) mirrors<br />
f is 5 for concave (converging) mirrors<br />
s is 1 for object to left of H<br />
s is 5 for object to right of H<br />
s″ is 5 for image to right of H″<br />
s″ is 1 for image to left of H″<br />
m is 1 for an inverted image<br />
m is 5 for an upright image<br />
rear focal point<br />
Note location of object and image relative to front and rear focal points.<br />
f = lens diameter<br />
m =<br />
s″/s = h″/h = magnification or<br />
conjugate ratio, said to be infinite if<br />
either s″ or s is infinite<br />
v = arcsin (f/2s)<br />
h = object height<br />
h″ = image height<br />
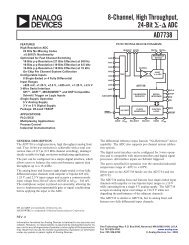
Sign conventions<br />
F″<br />
s″<br />
image<br />
s = object distance, positive for object (whether real<br />
or virtual) to the left of principal point H<br />
s″ = image distance (s and s″ are collectively called<br />
conjugate distances, with object and image in<br />
conjugate planes), positive for image (whether real<br />
or virtual) to the right of the principal point H″<br />
f = effective focal length (EFL) which may be positive<br />
(as shown) or negative. f represents both FH and<br />
H″F″, assuming lens to be surrounded by medium<br />
of index 1.0<br />
h″<br />
Fundamental Optics Gaussian Beam Optics <strong>Optical</strong> Specifications Material Properties <strong>Optical</strong> <strong>Coatings</strong><br />
Visit Us Online! www.mellesgriot.com 1 1.3