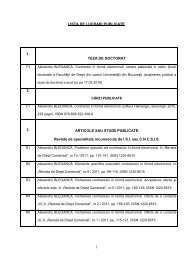
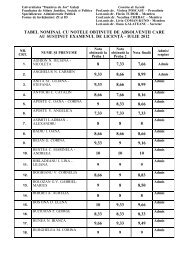
regional studies public administration - Facultatea de Drept ...
regional studies public administration - Facultatea de Drept ...
regional studies public administration - Facultatea de Drept ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION & REGIONAL STUDIES<br />
2nd Year, No. 1 – 2009<br />
Galati University Press, ISSN 2065 -1759<br />
On the other hand, the importance of the <strong>regional</strong> elements into<br />
the present socio-economic policies is very big.<br />
The growth of the <strong>regional</strong> policy’s importance is supported by<br />
two main phenomena. First, we assist to a powerful economic<br />
restructuration of the regions from the most <strong>de</strong>velopment E.U.’s<br />
countries as a consequence of the competition growth un<strong>de</strong>r<br />
globalisation. On the other hand, the new Member States from Central<br />
and Eastern Europe have immature market economies and some<br />
disequilibrium and dysfunctions occured after the moment of the<br />
adhering to the E.U.<br />
As a common element of these two processes, we can speak about<br />
the great efforts for the achievement of political and economic<br />
integration across the E.U. This objective implies a pertinent <strong>regional</strong><br />
policy.<br />
The quintessence of the European <strong>regional</strong> policy is the solidarity<br />
connected to the <strong>de</strong>crease in the <strong>regional</strong> <strong>de</strong>velopment disparities and<br />
the welfare of the European citizens. A real economic, social and<br />
territorial cohesion across the E.U. implies a<strong>de</strong>quate <strong>regional</strong> policy<br />
measures which have to be able to support the solving of the problems of<br />
the present E.U.: the industrial and agricultural areas in <strong>de</strong>cline, the<br />
disadvantaged urban areas, the unemployment, the criminality and the<br />
massive immigration.<br />
E.U. assigns 1/3 of its budget to the <strong>de</strong>crease of the disparities<br />
connected to the <strong>regional</strong> <strong>de</strong>velopment and the citizens’ welfare. This<br />
financial allocation became permanent after 1998, as a result of the<br />
growth of <strong>regional</strong> <strong>de</strong>velopment disparities. These disparities reflect the<br />
differences in the <strong>regional</strong> revenues differences (which can achieve a rate<br />
of 3:1) and the differences in the <strong>regional</strong>ly realised investments (with<br />
the same rate), which is worse.<br />
The implementation of <strong>regional</strong> policy is realised un<strong>de</strong>r the<br />
European, the national and the <strong>regional</strong> context. Practically, the common<br />
<strong>regional</strong> policy has to be implemented by each Member State using its<br />
specific instruments and ways. Moreover, the regions which represent<br />
the targets of the <strong>regional</strong> policy have to be stimulated in or<strong>de</strong>r to<br />
cooperate and to potent the material and financial efforts which are ma<strong>de</strong><br />
to achieve these objectives.<br />
On the other hand, the <strong>regional</strong> policy endorses some extracommunity<br />
objectives and regions, the <strong>de</strong>veloping countries, the<br />
candidate and the potential candidate states to the adhering, as well.<br />
95