Global Tuberculosis Control 2010 - Florida Department of Health
Global Tuberculosis Control 2010 - Florida Department of Health
Global Tuberculosis Control 2010 - Florida Department of Health
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
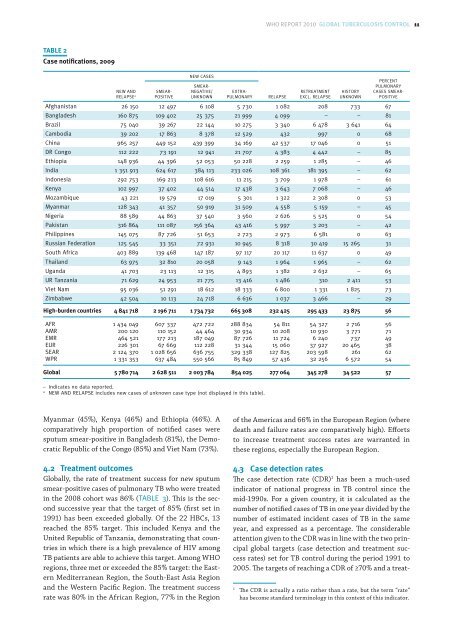
Myanmar (45%), Kenya (46%) and Ethiopia (46%). A<br />
comparatively high proportion <strong>of</strong> notified cases were<br />
sputum smear-positive in Bangladesh (81%), the Democratic<br />
Republic <strong>of</strong> the Congo (85%) and Viet Nam (73%).<br />
<br />
<strong>Global</strong>ly, the rate <strong>of</strong> treatment success for new sputum<br />
smear-positive cases <strong>of</strong> pulmonary TB who were treated<br />
in the 2008 cohort was 86% (). This is the second<br />
successive year that the target <strong>of</strong> 85% (first set in<br />
1991) has been exceeded globally. Of the 22 HBCs, 13<br />
reached the 85% target. This included Kenya and the<br />
United Republic <strong>of</strong> Tanzania, demonstrating that countries<br />
in which there is a high prevalence <strong>of</strong> HIV among<br />
TB patients are able to achieve this target. Among WHO<br />
regions, three met or exceeded the 85% target: the Eastern<br />
Mediterranean Region, the South-East Asia Region<br />
and the Western Pacific Region. The treatment success<br />
rate was 80% in the African Region, 77% in the Region<br />
<strong>of</strong> the Americas and 66% in the European Region (where<br />
death and failure rates are comparatively high). Efforts<br />
to increase treatment success rates are warranted in<br />
these regions, especially the European Region.<br />
<br />
The case detection rate (CDR) 1 has been a much-used<br />
indicator <strong>of</strong> national progress in TB control since the<br />
mid-1990s. For a given country, it is calculated as the<br />
number <strong>of</strong> notified cases <strong>of</strong> TB in one year divided by the<br />
number <strong>of</strong> estimated incident cases <strong>of</strong> TB in the same<br />
year, and expressed as a percentage. The considerable<br />
attention given to the CDR was in line with the two principal<br />
global targets (case detection and treatment success<br />
rates) set for TB control during the period 1991 to<br />
2005. The targets <strong>of</strong> reaching a CDR <strong>of</strong> ≥70% and a treat-<br />
1<br />
The CDR is actually a ratio rather than a rate, but the term “rate”<br />
has become standard terminology in this context <strong>of</strong> this indicator.