Brugia Malayi - Clark Science Center - Smith College
Brugia Malayi - Clark Science Center - Smith College
Brugia Malayi - Clark Science Center - Smith College
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Testing the Ability of SecretomeP Prediction Software to Predict<br />
<strong>Brugia</strong> malayi Secreted/Non-Secreted Proteins.<br />
Djénè Keita<br />
A<br />
B<br />
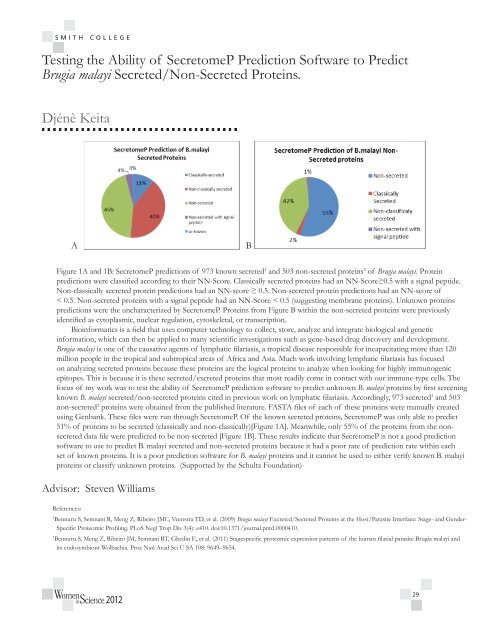
Figure 1A and 1B: SecretomeP predictions of 973 known secreted 1 and 503 non-secreted proteins 2 of <strong>Brugia</strong> malayi. Protein<br />
predictions were classified according to their NN-Score. Classically secreted proteins had an NN-Score≥0.5 with a signal peptide.<br />
Non-classically secreted protein predictions had an NN-score ≥ 0.5. Non-secreted protein predictions had an NN-score of<br />
< 0.5. Non-secreted proteins with a signal peptide had an NN-Score < 0.5 (suggesting membrane proteins). Unknown proteins<br />
predictions were the uncharacterized by SecretomeP. Proteins from Figure B within the non-secreted proteins were previously<br />
identified as cytoplasmic, nuclear regulation, cytoskeletal, or transcription.<br />
Bioinformatics is a field that uses computer technology to collect, store, analyze and integrate biological and genetic<br />
information, which can then be applied to many scientific investigations such as gene-based drug discovery and development.<br />
<strong>Brugia</strong> malayi is one of the causative agents of lymphatic filariasis, a tropical disease responsible for incapacitating more than 120<br />
million people in the tropical and subtropical areas of Africa and Asia. Much work involving lymphatic filariasis has focused<br />
on analyzing secreted proteins because these proteins are the logical proteins to analyze when looking for highly immunogenic<br />
epitopes. This is because it is these secreted/excreted proteins that most readily come in contact with our immune-type cells. The<br />
focus of my work was to test the ability of SecretomeP prediction software to predict unknown B. malayi proteins by first screening<br />
known B. malayi secreted/non-secreted proteins cited in previous work on lymphatic filariasis. Accordingly, 973 secreted 1 and 503<br />
non-secreted 2 proteins were obtained from the published literature. FASTA files of each of these proteins were manually created<br />
using Genbank. These files were run through SecretomeP. Of the known secreted proteins, SecretomeP was only able to predict<br />
51% of proteins to be secreted (classically and non-classically)[Figure 1A]. Meanwhile, only 55% of the proteins from the nonsecreted<br />
data file were predicted to be non-secreted [Figure 1B]. These results indicate that SecretomeP is not a good prediction<br />
software to use to predict B. malayi secreted and non-secreted proteins because it had a poor rate of prediction rate within each<br />
set of known proteins. It is a poor prediction software for B. malayi proteins and it cannot be used to either verify known B. malayi<br />
proteins or classify unknown proteins. (Supported by the Schultz Foundation)<br />
Advisor: Steven Williams<br />
References:<br />
1<br />
Bennuru S, Semnani R, Meng Z, Ribeiro JMC, Veenstra TD, et al. (2009) <strong>Brugia</strong> malayi Excreted/Secreted Proteins at the Host/Parasite Interface: Stage- and Gender-<br />
Specific Proteomic Profiling. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 3(4): e410. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0000410.<br />
2<br />
Bennuru S, Meng Z, Ribeiro JM, Semnani RT, Ghedin E, et al. (2011) Stagespecific proteomic expression patterns of the human filarial parasite <strong>Brugia</strong> malayi and<br />
its endosymbiont Wolbachia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U SA 108: 9649–9654.<br />
2012<br />
29