Got Food? - the Scientia Review
Got Food? - the Scientia Review
Got Food? - the Scientia Review
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Arrhythmia<br />
In a healthy human heart, all of <strong>the</strong> signals coordinate in a way that maintains <strong>the</strong> synchronous<br />
beating of muscle cells. However, occasionally problems develop with <strong>the</strong> electrical activity in <strong>the</strong> heart<br />
as <strong>the</strong> result of certain diseases or genetics. Personal lifestyle choices such as diet and exercise also play a<br />
critical role in <strong>the</strong> development of cardiac issues (Berry et al., 2012).<br />
Over 600,000 people are hospitalized every year for cardiac dysrhythmias, also known as<br />
arrhythmias or irregular heartbeat. A person with an arrhythmia has abnormal electrical activity in <strong>the</strong><br />
heart, and <strong>the</strong>refore an unnatural heart rhythm. There are two main types of arrhythmias: bradycardia, in<br />
which <strong>the</strong> heart has less than 60 beats per minute; and tachycardia, in which <strong>the</strong> heart has more than 100<br />
beats per minute. The first step in diagnosing an arrhythmia is determining where in <strong>the</strong> heart it<br />
originates. Once this is determined, specific treatment can be given to that region of <strong>the</strong> heart, if possible.<br />
There are several treatment options available to patients with arrhythmias including medicine,<br />
implantation of a pacemaker, anticoagulants (to reduce <strong>the</strong> risk of blood clots), cardiac defibrillation, and<br />
cardiac ablation (―Your heart's electrical system‖, 2008).<br />
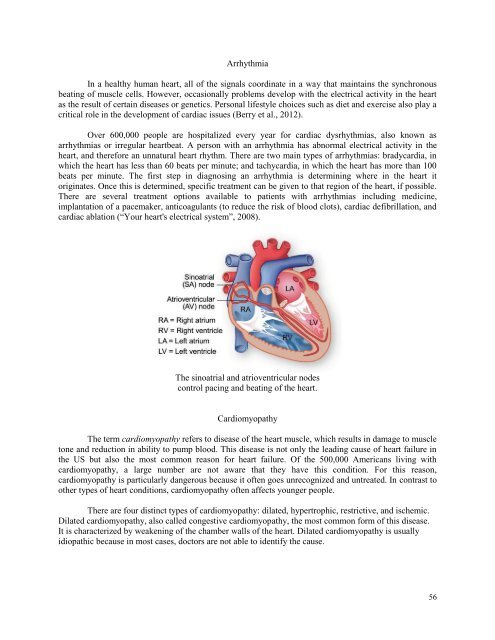
The sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes<br />
control pacing and beating of <strong>the</strong> heart.<br />
Cardiomyopathy<br />
The term cardiomyopathy refers to disease of <strong>the</strong> heart muscle, which results in damage to muscle<br />
tone and reduction in ability to pump blood. This disease is not only <strong>the</strong> leading cause of heart failure in<br />
<strong>the</strong> US but also <strong>the</strong> most common reason for heart failure. Of <strong>the</strong> 500,000 Americans living with<br />
cardiomyopathy, a large number are not aware that <strong>the</strong>y have this condition. For this reason,<br />
cardiomyopathy is particularly dangerous because it often goes unrecognized and untreated. In contrast to<br />
o<strong>the</strong>r types of heart conditions, cardiomyopathy often affects younger people.<br />
There are four distinct types of cardiomyopathy: dilated, hypertrophic, restrictive, and ischemic.<br />
Dilated cardiomyopathy, also called congestive cardiomyopathy, <strong>the</strong> most common form of this disease.<br />
It is characterized by weakening of <strong>the</strong> chamber walls of <strong>the</strong> heart. Dilated cardiomyopathy is usually<br />
idiopathic because in most cases, doctors are not able to identify <strong>the</strong> cause.<br />
56