A guide for the preparation and use of buffers in biological systems
A guide for the preparation and use of buffers in biological systems
A guide for the preparation and use of buffers in biological systems
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
concentration is dependent upon <strong>the</strong> amount <strong>of</strong> dissolved carbon dioxide <strong>the</strong><br />
ultimate buffer<strong>in</strong>g capacity is dependent upon <strong>the</strong> amount <strong>of</strong> bicarbonate <strong>and</strong><br />
<strong>the</strong> partial pressure <strong>of</strong> carbon dioxide.<br />
+ _<br />
H + HCO 3<br />
H 2<br />
CO 2<br />
H 2<br />
OCO 2<br />
H 2<br />
O<br />
CO 2<br />
Blood<br />
Lung<br />
Air Space<br />
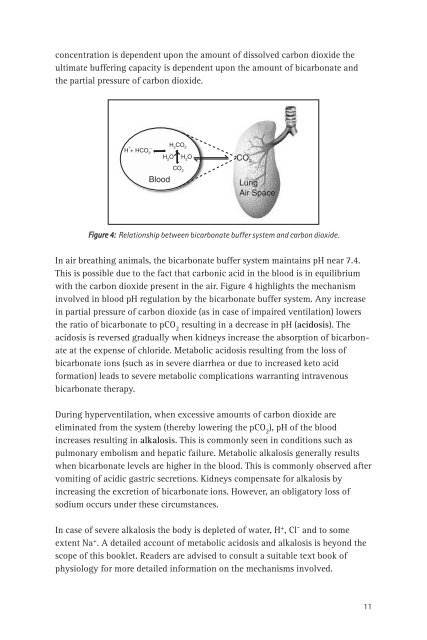
Figure 4: Relationship between bicarbonate buffer system <strong>and</strong> carbon dioxide.<br />
In air breath<strong>in</strong>g animals, <strong>the</strong> bicarbonate buffer system ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong>s pH near 7.4.<br />
This is possible due to <strong>the</strong> fact that carbonic acid <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> blood is <strong>in</strong> equilibrium<br />
with <strong>the</strong> carbon dioxide present <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> air. Figure 4 highlights <strong>the</strong> mechanism<br />
<strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong> blood pH regulation by <strong>the</strong> bicarbonate buffer system. Any <strong>in</strong>crease<br />
<strong>in</strong> partial pressure <strong>of</strong> carbon dioxide (as <strong>in</strong> case <strong>of</strong> impaired ventilation) lowers<br />
<strong>the</strong> ratio <strong>of</strong> bicarbonate to pCO 2<br />
result<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> a decrease <strong>in</strong> pH (acidosis). The<br />
acidosis is reversed gradually when kidneys <strong>in</strong>crease <strong>the</strong> absorption <strong>of</strong> bicarbonate<br />
at <strong>the</strong> expense <strong>of</strong> chloride. Metabolic acidosis result<strong>in</strong>g from <strong>the</strong> loss <strong>of</strong><br />
bicarbonate ions (such as <strong>in</strong> severe diarrhea or due to <strong>in</strong>creased keto acid<br />
<strong>for</strong>mation) leads to severe metabolic complications warrant<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>travenous<br />
bicarbonate <strong>the</strong>rapy.<br />
Dur<strong>in</strong>g hyperventilation, when excessive amounts <strong>of</strong> carbon dioxide are<br />
elim<strong>in</strong>ated from <strong>the</strong> system (<strong>the</strong>reby lower<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> pCO 2<br />
), pH <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> blood<br />
<strong>in</strong>creases result<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> alkalosis. This is commonly seen <strong>in</strong> conditions such as<br />
pulmonary embolism <strong>and</strong> hepatic failure. Metabolic alkalosis generally results<br />
when bicarbonate levels are higher <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> blood. This is commonly observed after<br />
vomit<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> acidic gastric secretions. Kidneys compensate <strong>for</strong> alkalosis by<br />
<strong>in</strong>creas<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> excretion <strong>of</strong> bicarbonate ions. However, an obligatory loss <strong>of</strong><br />
sodium occurs under <strong>the</strong>se circumstances.<br />
In case <strong>of</strong> severe alkalosis <strong>the</strong> body is depleted <strong>of</strong> water, H + , Cl¯ <strong>and</strong> to some<br />
extent Na + . A detailed account <strong>of</strong> metabolic acidosis <strong>and</strong> alkalosis is beyond <strong>the</strong><br />
scope <strong>of</strong> this booklet. Readers are advised to consult a suitable text book <strong>of</strong><br />
physiology <strong>for</strong> more detailed <strong>in</strong><strong>for</strong>mation on <strong>the</strong> mechanisms <strong>in</strong>volved.<br />
11