Fortron PPS Product Brochure (B240) - Hi Polymers
Fortron PPS Product Brochure (B240) - Hi Polymers
Fortron PPS Product Brochure (B240) - Hi Polymers
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Fortron</strong> ®<br />
Polyphenylene sulphide (<strong>PPS</strong>)<br />
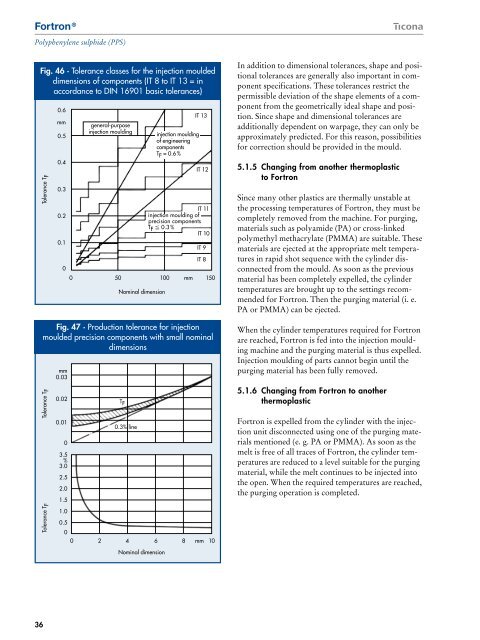
Fig. 46 · Tolerance classes for the injection moulded<br />
dimensions of components (IT 8 to IT 13 = in<br />
accordance to DIN 16901 basic tolerances)<br />
Tolerance T F<br />
0.6<br />
mm<br />
0.5<br />
0.4<br />
0.3<br />
0.2<br />
0.1<br />
general-purpose<br />
injection moulding<br />
IT 8<br />
0<br />
0 50 100 mm 150<br />
Nominal dimension<br />
injection moulding<br />
of engineering<br />
components<br />
T F = 0.6 %<br />
IT 13<br />
IT 12<br />
IT 11<br />
injection moulding of<br />
precision components<br />
T F 0.3 %<br />
IT 10<br />
IT 9<br />
Fig. 47 · <strong>Product</strong>ion tolerance for injection<br />
moulded precision components with small nominal<br />
dimensions<br />
Tolerance T F<br />
Tolerance T F<br />
mm<br />
0.03<br />
0.02<br />
0.01<br />
0<br />
3.5<br />
%<br />
3.0<br />
2.5<br />
2.0<br />
1.5<br />
1.0<br />
T F<br />
0.3% line<br />
0.5<br />
0<br />
0 2 4 6 8 mm 10<br />
In addition to dimensional tolerances, shape and positional<br />
tolerances are generally also important in component<br />
specifications. These tolerances restrict the<br />
permissible deviation of the shape elements of a component<br />
from the geometrically ideal shape and position.<br />
Since shape and dimensional tolerances are<br />
additionally dependent on warpage, they can only be<br />
approximately predicted. For this reason, possibilities<br />
for correction should be provided in the mould.<br />
5.1.5 Changing from another thermoplastic<br />
to <strong>Fortron</strong><br />
Since many other plastics are thermally unstable at<br />
the processing temperatures of <strong>Fortron</strong>, they must be<br />
completely removed from the machine. For purging,<br />
materials such as polyamide (PA) or cross-linked<br />
polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) are suitable. These<br />
materials are ejected at the appropriate melt temperatures<br />
in rapid shot sequence with the cylinder disconnected<br />
from the mould. As soon as the previous<br />
material has been completely expelled, the cylinder<br />
temperatures are brought up to the settings recommended<br />
for <strong>Fortron</strong>. Then the purging material (i. e.<br />
PA or PMMA) can be ejected.<br />
When the cylinder temperatures required for <strong>Fortron</strong><br />
are reached, <strong>Fortron</strong> is fed into the injection moulding<br />
machine and the purging material is thus expelled.<br />
Injection moulding of parts cannot begin until the<br />
purging material has been fully removed.<br />
5.1.6 Changing from <strong>Fortron</strong> to another<br />
thermoplastic<br />
<strong>Fortron</strong> is expelled from the cylinder with the injection<br />
unit disconnected using one of the purging materials<br />
mentioned (e. g. PA or PMMA). As soon as the<br />
melt is free of all traces of <strong>Fortron</strong>, the cylinder temperatures<br />
are reduced to a level suitable for the purging<br />
material, while the melt continues to be injected into<br />
the open. When the required temperatures are reached,<br />
the purging operation is completed.<br />
Nominal dimension<br />
36