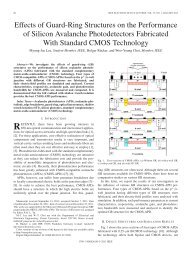
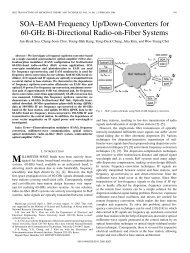
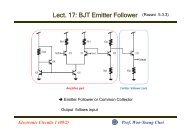
10Gbps Optical Receiver and VCSEL Driver in 0.13um CMOS ...
10Gbps Optical Receiver and VCSEL Driver in 0.13um CMOS ...
10Gbps Optical Receiver and VCSEL Driver in 0.13um CMOS ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Noise Current,<br />
i rms<br />
n,TIA<br />
(f), is determ<strong>in</strong>ed by <strong>in</strong>tegrat<strong>in</strong>g the output-referred<br />
noise spectrum up at least 2 x BW 3-dB <strong>and</strong> divid<strong>in</strong>g it by the passb<strong>and</strong><br />
transimpedance value. Written <strong>in</strong> the squared form, we have:<br />
i<br />
2<br />
n , TIA<br />
1 2<br />
2<br />
= ZT<br />
( f ) ⋅ In,<br />
TIA(<br />
f ) df<br />
2 ∫ (2.4)<br />
Z<br />
T<br />
where |Z T (f)| is the frequency response of the transimpedance. The total<br />
<strong>in</strong>put-referred noise current directly determ<strong>in</strong>es the sensitivity of the<br />
TIA:<br />
pp<br />
rms<br />
i<br />
S<br />
2Q<br />
⋅ In,<br />
TIA<br />
= (2.5)<br />
where Q is the quality factor for desired bit error rates (BERs). The<br />
Averaged Input-Referred Noise Current Density is def<strong>in</strong>ed as the <strong>in</strong>put-<br />
rms<br />
referred rms noise current, , divided by the square-root of the 3-<br />
dB b<strong>and</strong>width. Aga<strong>in</strong>, it is important that the averag<strong>in</strong>g is carried out<br />
over the output-referred noise spectrum rather than the <strong>in</strong>put-referred<br />
noise spectrum, .<br />
I 2 n,<br />
TIA<br />
i<br />
n , TIA<br />
2.1.2.2 TIA Topologies<br />
Generally there are two types of TIA topologies, open loop TIAs<br />
12