Major Health Issues in Nova Scotia: An Environmental Scan
Major Health Issues in Nova Scotia: An Environmental Scan
Major Health Issues in Nova Scotia: An Environmental Scan
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
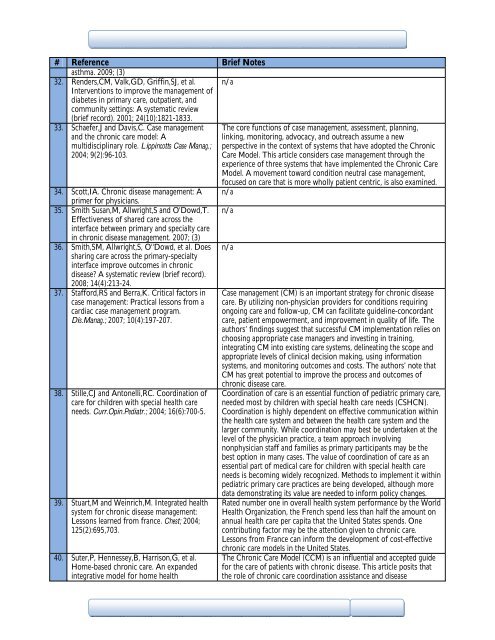
# Reference Brief Notes<br />
asthma. 2009; (3)<br />
32. Renders,CM, Valk,GD, Griff<strong>in</strong>,SJ, et al. n/a<br />
Interventions to improve the management of<br />
diabetes <strong>in</strong> primary care, outpatient, and<br />
community sett<strong>in</strong>gs: A systematic review<br />
(brief record). 2001; 24(10):1821-1833.<br />
33. Schaefer,J and Davis,C. Case management<br />
and the chronic care model: A<br />
multidiscipl<strong>in</strong>ary role. Lipp<strong>in</strong>cotts Case Manag.;<br />
2004; 9(2):96-103.<br />
The core functions of case management, assessment, plann<strong>in</strong>g,<br />
l<strong>in</strong>k<strong>in</strong>g, monitor<strong>in</strong>g, advocacy, and outreach assume a new<br />
perspective <strong>in</strong> the context of systems that have adopted the Chronic<br />
Care Model. This article considers case management through the<br />
experience of three systems that have implemented the Chronic Care<br />
Model. A movement toward condition neutral case management,<br />
focused on care that is more wholly patient centric, is also exam<strong>in</strong>ed.<br />
34. Scott,IA. Chronic disease management: A n/a<br />
primer for physicians.<br />
35. Smith Susan,M, Allwright,S and O'Dowd,T. n/a<br />
Effectiveness of shared care across the<br />
<strong>in</strong>terface between primary and specialty care<br />
<strong>in</strong> chronic disease management. 2007; (3)<br />
36. Smith,SM, Allwright,S, O''Dowd, et al. Does<br />
shar<strong>in</strong>g care across the primary-specialty<br />
<strong>in</strong>terface improve outcomes <strong>in</strong> chronic<br />
disease? A systematic review (brief record).<br />
n/a<br />
2008; 14(4):213-24.<br />
37. Stafford,RS and Berra,K. Critical factors <strong>in</strong><br />
case management: Practical lessons from a<br />
cardiac case management program.<br />
Dis.Manag.; 2007; 10(4):197-207.<br />
38. Stille,CJ and <strong>An</strong>tonelli,RC. Coord<strong>in</strong>ation of<br />
care for children with special health care<br />
needs. Curr.Op<strong>in</strong>.Pediatr.; 2004; 16(6):700-5.<br />
39. Stuart,M and We<strong>in</strong>rich,M. Integrated health<br />
system for chronic disease management:<br />
Lessons learned from france. Chest; 2004;<br />
125(2):695,703.<br />
40. Suter,P, Hennessey,B, Harrison,G, et al.<br />
Home-based chronic care. <strong>An</strong> expanded<br />
<strong>in</strong>tegrative model for home health<br />
Case management (CM) is an important strategy for chronic disease<br />
care. By utiliz<strong>in</strong>g non-physician providers for conditions requir<strong>in</strong>g<br />
ongo<strong>in</strong>g care and follow-up, CM can facilitate guidel<strong>in</strong>e-concordant<br />
care, patient empowerment, and improvement <strong>in</strong> quality of life. The<br />
authors’ f<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>gs suggest that successful CM implementation relies on<br />
choos<strong>in</strong>g appropriate case managers and <strong>in</strong>vest<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g,<br />
<strong>in</strong>tegrat<strong>in</strong>g CM <strong>in</strong>to exist<strong>in</strong>g care systems, del<strong>in</strong>eat<strong>in</strong>g the scope and<br />
appropriate levels of cl<strong>in</strong>ical decision mak<strong>in</strong>g, us<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
systems, and monitor<strong>in</strong>g outcomes and costs. The authors’ note that<br />
CM has great potential to improve the process and outcomes of<br />
chronic disease care.<br />
Coord<strong>in</strong>ation of care is an essential function of pediatric primary care,<br />
needed most by children with special health care needs (CSHCN).<br />
Coord<strong>in</strong>ation is highly dependent on effective communication with<strong>in</strong><br />
the health care system and between the health care system and the<br />
larger community. While coord<strong>in</strong>ation may best be undertaken at the<br />
level of the physician practice, a team approach <strong>in</strong>volv<strong>in</strong>g<br />
nonphysician staff and families as primary participants may be the<br />
best option <strong>in</strong> many cases. The value of coord<strong>in</strong>ation of care as an<br />
essential part of medical care for children with special health care<br />
needs is becom<strong>in</strong>g widely recognized. Methods to implement it with<strong>in</strong><br />
pediatric primary care practices are be<strong>in</strong>g developed, although more<br />
data demonstrat<strong>in</strong>g its value are needed to <strong>in</strong>form policy changes.<br />
Rated number one <strong>in</strong> overall health system performance by the World<br />
<strong>Health</strong> Organization, the French spend less than half the amount on<br />
annual health care per capita that the United States spends. One<br />
contribut<strong>in</strong>g factor may be the attention given to chronic care.<br />
Lessons from France can <strong>in</strong>form the development of cost-effective<br />
chronic care models <strong>in</strong> the United States.<br />
The Chronic Care Model (CCM) is an <strong>in</strong>fluential and accepted guide<br />
for the care of patients with chronic disease. This article posits that<br />
the role of chronic care coord<strong>in</strong>ation assistance and disease