“A Stitch in Time...”
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
With a background now of how time affects the mean<strong>in</strong>g of <strong>in</strong>strument<br />
read<strong>in</strong>gs, let’s consider three common test methods: (1) short-time or spot<br />
read<strong>in</strong>g; (2) time-resistance; and (3) step or multi-voltage tests.<br />
Types of Insulation Resistance Tests<br />
Short-<strong>Time</strong> or Spot-Read<strong>in</strong>g Test<br />
In this method, you simply connect the Megger <strong>in</strong>strument across the<br />
<strong>in</strong>sulation to be tested and operate it for a short, specific time period<br />
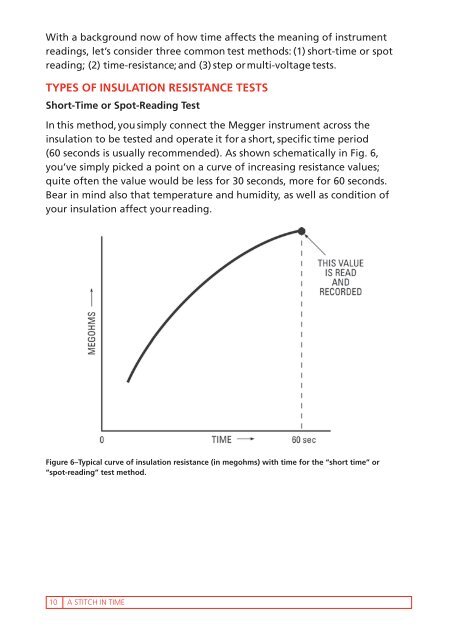
(60 seconds is usually recommended). As shown schematically <strong>in</strong> Fig. 6,<br />
you’ve simply picked a po<strong>in</strong>t on a curve of <strong>in</strong>creas<strong>in</strong>g resistance values;<br />
quite often the value would be less for 30 seconds, more for 60 seconds.<br />
Bear <strong>in</strong> m<strong>in</strong>d also that temperature and humidity, as well as condition of<br />
your <strong>in</strong>sulation affect your read<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
Figure 6–Typical curve of <strong>in</strong>sulation resistance (<strong>in</strong> megohms) with time for the “short time<strong>”</strong> or<br />
“spot-read<strong>in</strong>g<strong>”</strong> test method.<br />
10<br />
A STITCH IN TIME