Lab & Pre-lab #11
Lab & Pre-lab #11
Lab & Pre-lab #11
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Lenses and Images v 0.1<br />
a<br />
b<br />
Image<br />
Object<br />
f<br />
f<br />
c<br />
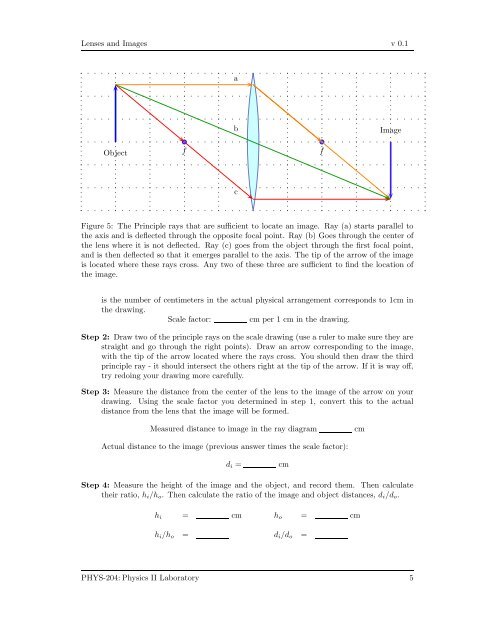
Figure 5: The Principle rays that are sufficient to locate an image. Ray (a) starts parallel to<br />
the axis and is deflected through the opposite focal point. Ray (b) Goes through the center of<br />
the lens where it is not deflected. Ray (c) goes from the object through the first focal point,<br />
and is then deflected so that it emerges parallel to the axis. The tip of the arrow of the image<br />
is located where these rays cross. Any two of these three are sufficient to find the location of<br />
the image.<br />
is the number of centimeters in the actual physical arrangement corresponds to 1cm in<br />
the drawing.<br />
Scale factor: cm per 1 cm in the drawing.<br />
Step 2: Draw two of the principle rays on the scale drawing (use a ruler to make sure they are<br />
straight and go through the right points). Draw an arrow corresponding to the image,<br />
with the tip of the arrow located where the rays cross. You should then draw the third<br />
principle ray - it should intersect the others right at the tip of the arrow. If it is way off,<br />
try redoing your drawing more carefully.<br />
Step 3: Measure the distance from the center of the lens to the image of the arrow on your<br />
drawing. Using the scale factor you determined in step 1, convert this to the actual<br />
distance from the lens that the image will be formed.<br />
Measured distance to image in the ray diagram<br />
cm<br />
Actual distance to the image (previous answer times the scale factor):<br />
d i =<br />
cm<br />
Step 4: Measure the height of the image and the object, and record them. Then calculate<br />
their ratio, h i /h o . Then calculate the ratio of the image and object distances, d i /d o .<br />
h i = cm h o = cm<br />
h i /h o = d i /d o =<br />
PHYS-204: Physics II <strong>Lab</strong>oratory 5