Lab & Pre-lab #11
Lab & Pre-lab #11
Lab & Pre-lab #11
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
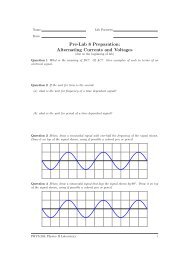
Lenses and Images v 0.1<br />
Step 5: Measure the height of the image, h i , and the height of the object, h o , and record these.<br />
Also note whether the object is inverted or erect. Then calculate the ratios of the image<br />
and object heights, and the image and object distances.<br />
measured: h i = cm measured: h o = cm<br />
measured: h i /h o = measured: d i /d o =<br />
Question 1.6 Is the ratio of the measured heights of the image and object nearly equal<br />
to the ratio of the measured distances Again, discuss the accuracy with which you could<br />
measure these quantities to draw a fair conclusion about their equality.<br />
There is an algebraic equation that relates the object distance, d 0 , (the distance from<br />
the lens to the object), the image distance, d i , (distance from lens to the position of the<br />
image), and the focal length, f, of the lens. This relationship involves the power of the<br />
lens, which is inversely proportional to the focal length (shorter focal length means greater<br />
power).<br />
1<br />
+ 1 = 1 thin lens formula<br />
d o d i f<br />
.<br />
Question 1.7 Using the formula above calculate the image distance given that f = 15cm,<br />
and d o = 20cm. Compare this with your measured value, again taking into account the<br />
precision in your measurement of the image and object distances.<br />
Measured: d i =<br />
cm.<br />
<strong>Pre</strong>diction 1.2 What will happen if the distance from the lens to the object is increased<br />
Will the image distance get shorter or longer Will the image get larger or smaller To<br />
make this prediction, make a ray diagram with the object farther from the lens than the<br />
previous one. A scale drawing is provided in Fig. 7.<br />
Now test your predictions.<br />
Step 6: Move the lens so that it is at least 30cm from the F-diaphragm.<br />
Step 7: Move the white screen until you find a position at which a clear image is formed.<br />
Step 8: Measure the object and image distances, and the height of the object and image.<br />
Record the measurements below.<br />
d i = cm d o = cm<br />
h i = cm h o = cm<br />
PHYS-204: Physics II <strong>Lab</strong>oratory 7