Granger-causality tests
Granger-causality tests
Granger-causality tests
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Tools<br />
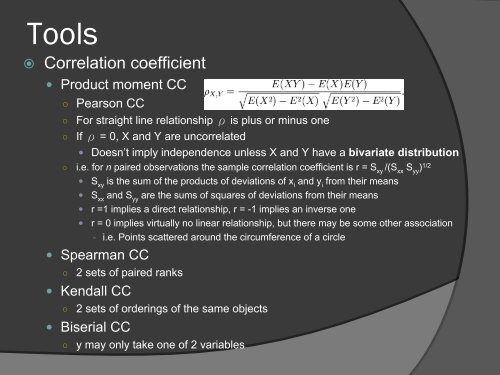
Correlation coefficient<br />
• Product moment CC<br />
○ Pearson CC<br />
○<br />
○<br />
For straight line relationship ρ is plus or minus one<br />
If ρ = 0, X and Y are uncorrelated<br />
• Doesn’t imply independence unless X and Y have a bivariate distribution<br />
○ i.e. for n paired observations the sample correlation coefficient is r = S xy<br />
/(S xx<br />
S yy<br />
) 1/2<br />
• S xy<br />
is the sum of the products of deviations of x i<br />
and y i<br />
from their means<br />
• S xx<br />
and S yy<br />
are the sums of squares of deviations from their means<br />
• r =1 implies a direct relationship, r = -1 implies an inverse one<br />
• r = 0 implies virtually no linear relationship, but there may be some other association<br />
- i.e. Points scattered around the circumference of a circle<br />
• Spearman CC<br />
○<br />
2 sets of paired ranks<br />
• Kendall CC<br />
○<br />
2 sets of orderings of the same objects<br />
• Biserial CC<br />
○<br />
y may only take one of 2 variables