- Page 3 and 4: Message from the PresidentIn cooper
- Page 5 and 6: ¡X-ray crystallographic studies of
- Page 7 and 8: Topics of Research in This YearComp
- Page 9 and 10: Elucidation of genomic structure ar
- Page 11 and 12: the total library) were mapped onto
- Page 13 and 14: observed among the ribosomal protei
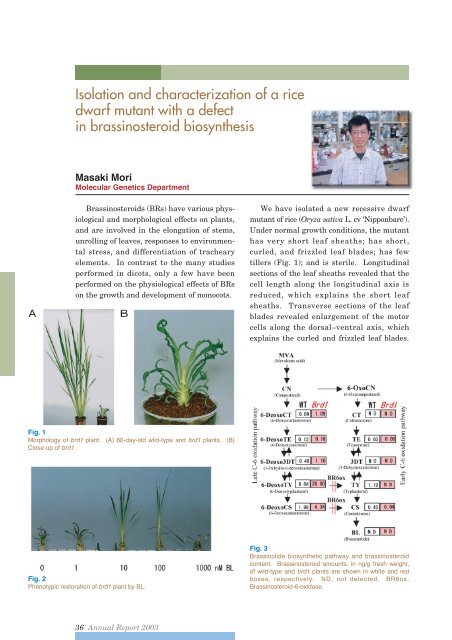
- Page 15 and 16: molecular analyses and morphologica
- Page 17 and 18: with 5 IU equine chorionic gonadotr
- Page 19 and 20: serious problem in rice production
- Page 21 and 22: exogenous genes into a hymenopteran
- Page 23 and 24: Isolation and characterization of B
- Page 25 and 26: oids could be regenerated from endo
- Page 27 and 28: Quantitative trait locus analyses o
- Page 29 and 30: ion, induces hypercholesterolemia,
- Page 31 and 32: is an important source for amino ac
- Page 33 and 34: In this study, 1.4 and 1.6 kb-long
- Page 35 and 36: aqueous solution using cyanuric chl
- Page 37 and 38: Developing a waste selection device
- Page 39 and 40: decreased every five days by 5˚C,
- Page 41: ticides. If the viral dose that kil
- Page 45 and 46: Molecular structure of the GARP fam
- Page 47 and 48: X-ray crystallographic studies ofSt
- Page 49 and 50: Rapid and high resolution QTL analy
- Page 51 and 52: Plant regeneration system through m
- Page 53 and 54: Table 1 Transformation Efficiency a
- Page 55 and 56: from the tissues of mutants. The In
- Page 57 and 58: the regenerated plants were transpl
- Page 59 and 60: plants and fungi, and RNA interfere
- Page 61 and 62: eeding, classification of microbes
- Page 63 and 64: efforts are made to obtain single m
- Page 65 and 66: was carried out by shotgun sequenci
- Page 67 and 68: epetitive sequence specific to Oryz
- Page 69 and 70: 75 µM of ABA at 25ºC. More than 8
- Page 71 and 72: Change of the molecular weightforms
- Page 73 and 74: A unique landrace group recognizedb
- Page 75 and 76: eaction (PCR) primer pairs to detec
- Page 77 and 78: This was the first successful case
- Page 79 and 80: to disappear by degradation or dilu
- Page 81 and 82: tained 1933 independent genes and b
- Page 83 and 84: that antigen-specific regulatory T
- Page 85 and 86: neural activity patterns evoked by
- Page 87 and 88: considerable effect on the suscepti
- Page 89 and 90: Insect Genetics and Evolution Depar
- Page 91 and 92: activity, which was found to detoxi
- Page 93 and 94:
Insect Biomaterial and Technology D
- Page 95 and 96:
peptides obtained from sericin a re
- Page 97 and 98:
DNA markers for Nid-1, a resistance
- Page 99 and 100:
or carotenoid pigment. When sericin
- Page 101 and 102:
Plant Science DivisionThe Plant Sci
- Page 103 and 104:
mutants have been studied in relati
- Page 105 and 106:
have verified that candidate genes
- Page 107 and 108:
and C, connected by a distorted typ
- Page 109 and 110:
mammalian cells, respectively, inhi
- Page 111 and 112:
undle sheath cells (BSCs), the land
- Page 113 and 114:
(OsNHX1), barley (HvNHX1) and baril
- Page 115 and 116:
nation rates. However, in our attem
- Page 117 and 118:
Yeast two-hybrid assay showed inter
- Page 119 and 120:
and a few NADPH-cytochrome P450 oxi
- Page 121 and 122:
the R0(53%).Foreign genes (35S + np
- Page 123 and 124:
gamma ray from 44 TBq 60 Co was use
- Page 125 and 126:
List of PublicationOriginal Papers1
- Page 127 and 128:
35 Fujisaki S, Mizoguchi Y, Takahas
- Page 129 and 130:
71 Imai K, Khandoker MY, Yonai M, T
- Page 131 and 132:
107 Kiuchi S, Inage Y, Hiraiwa H, U
- Page 133 and 134:
147 Miyamoto Y, Sakumoto R, Sakabe
- Page 135 and 136:
184 Ochi A, Hossain KS, Magoshi J,
- Page 137 and 138:
219 Takahashi M, Nagai T, Okamura N
- Page 139 and 140:
258 Watanabe H, Nakashima K, Saito
- Page 141 and 142:
Author Department Paper.No.Yasushi
- Page 143 and 144:
Author Department Paper.No.Sadao Wa
- Page 145 and 146:
Monograph1 Magoshi J, Nakamura S (2
- Page 147 and 148:
on Lepidopteran Genomics”.NIAS-CO
- Page 149 and 150:
tion of the high-quality draft sequ
- Page 151 and 152:
Executive Members andResearch Staff
- Page 153 and 154:
Insect Growth Regulation Laboratory
- Page 155 and 156:
Sericultural Science LaboratoryMole
- Page 157 and 158:
Members of NIAS EvaluationComittee(
- Page 159 and 160:
Annual Report 2003 153