Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
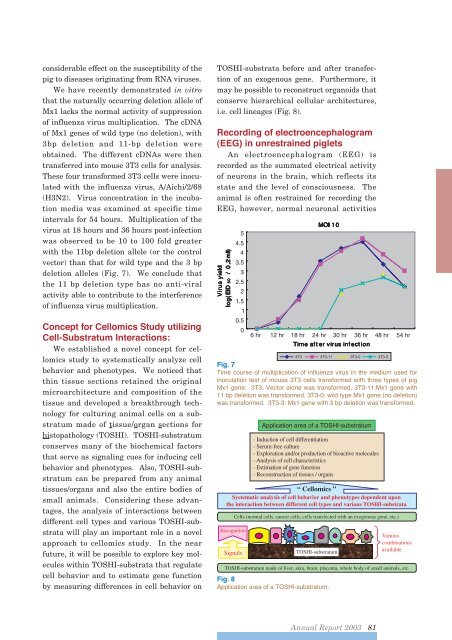
considerable effect on the susceptibility of thepig to diseases originating from RNA viruses.We have recently demonstrated in vitrothat the naturally occurring deletion allele ofMx1 lacks the normal activity of suppressionof influenza virus multiplication. The cDNAof Mx1 genes of wild type (no deletion), with3bp deletion and 11-bp deletion wereobtained. The different cDNAs were thentransferred into mouse 3T3 cells for analysis.These four transformed 3T3 cells were inoculatedwith the influenza virus, A/Aichi/2/68(H3N2). Virus concentration in the incubationmedia was examined at specific timeintervals for 54 hours. Multiplication of thevirus at 18 hours and 36 hours post-infectionwas observed to be 10 to 100 fold greaterwith the 11bp deletion allele (or the controlvector) than that for wild type and the 3 bpdeletion alleles (Fig. 7). We conclude thatthe 11 bp deletion type has no anti-viralactivity able to contribute to the interferenceof influenza virus multiplication.Concept for Cellomics Study utilizingCell-Substratum Interactions:We established a novel concept for cellomicsstudy to systematically analyze cellbehavior and phenotypes. We noticed thatthin tissue sections retained the originalmicroarchitecture and composition of thetissue and developed a breakthrough technologyfor culturing animal cells on a substratummade of tissue/organ sections forhistopathology (TOSHI). TOSHI-substratumconserves many of the biochemical factorsthat serve as signaling cues for inducing cellbehavior and phenotypes. Also, TOSHI-substratumcan be prepared from any animaltissues/organs and also the entire bodies ofsmall animals. Considering these advantages,the analysis of interactions betweendifferent cell types and various TOSHI-substratawill play an important role in a novelapproach to cellomics study. In the nearfuture, it will be possible to explore key moleculeswithin TOSHI-substrata that regulatecell behavior and to estimate gene functionby measuring differences in cell behavior onTOSHI-substrata before and after transfectionof an exogenous gene. Furthermore, itmay be possible to reconstruct organoids thatconserve hierarchical cellular architectures,i.e. cell lineages (Fig. 8).Recording of electroencephalogram(EEG) in unrestrained pigletsAn electroencephalogram (EEG) isrecorded as the summated electrical activityof neurons in the brain, which reflects itsstate and the level of consciousness. Theanimal is often restrained for recording theEEG, however, normal neuronal activitiesFig. 7Time course of multiplication of influenza virus in the medium used forinoculation test of mouse 3T3 cells transformed with three types of pigMx1 gene. 3T3: Vector alone was transformed, 3T3-11:Mx1 gene with11 bp deletion was transformed, 3T3-0: wild type Mx1 gene (no deletion)was transformed. 3T3-3: Mx1 gene with 3 bp deletion was transformed.Application area of a TOSHI-substratum- Induction of cell differentiation- Serum-free culture- Exploration and/or production of bioactive molecules- Analysis of cell characteristics- Estimation of gene function- Reconstruction of tissues / organs“ Cellomics ”Systematic analysis of cell behavior and phenotypes dependent uponthe interaction between different cell types and various TOSHI-substrataRecognitionSignalsCells (normal cells, cancer cells, cells transfected with an exogenous gene, etc.)TOSHI-substratumTOSHI-substratum made of liver, skin, brain, placenta, whole body of small animals, etc.Fig. 8Application area of a TOSHI-substratum.Variouscombinationsavailable<strong>Annual</strong> <strong>Report</strong> <strong>2003</strong> 81