Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Twin studies as a strategy to<br />
identify quantitative trait loci<br />
Andreas Busjahn and Hans-Dieter<br />
Faulhaber have recruited over 200<br />
pairs of monozygotic (MZ) and 120<br />
dizygotic (DZ) normotensive young<br />
twins and the parents of the DZ twins.<br />
The subjects were carefully phenotyped<br />
in terms of blood pressure, blood<br />
pressure in response to provocative<br />
maneuvers, psychological testing, and<br />
serum lipid concentrations. The<br />
strategy is to use a standard twin<br />
analysis to determine heritability<br />
estimates and to distinguish between<br />
hereditary and environmental<br />
influences. This allows us to perform<br />
a standard IBD linkage analysis in the<br />
DZ twins and their parents, as well as<br />
association studies in the entire twin<br />
cohort.<br />
With this approach, we recently<br />
identified a series of quantitative trait<br />
loci (QTL) relevant to blood pressure<br />
regulation. The strongest linkage was<br />
found to the IGF-1 gene locus. In<br />
collaboration with Margret Hoehe, we<br />
have gained new insight into the<br />
contribution of the β-2 adrenergic<br />
receptor gene. Margret Hoehe’s team<br />
sequenced the entire β-2 adrenergic<br />
receptor gene in our twin cohort and<br />
found 15 SNPs, including numerous<br />
new mutations. Finally, we have an<br />
active cooperation with Per Lund-<br />
Johansen’s group in Bergen, Norway.<br />
From the Bergen Hypertension Study,<br />
we have genotyped offspring from<br />
two normotensive and hypertensive<br />
parents and have been able to<br />
associate the Arg16->Gly variant to<br />
blood pressure in this cohort.<br />
We have used the QTL approach to<br />
show that the loci for the long QTc<br />
genes, which code for ion channels<br />
and their regulators, are all linked to<br />
electrocardiogram components. The<br />
long QTc syndromes are monogenic<br />
diseases associated with sudden<br />
cardiac death. Showing relevance of<br />
these genes to arrhythmias or risk of<br />
arrhythmias in the general population,<br />
is the first step in identifying common<br />
variants indicating a risk to ventricular<br />
arrhythmia. The topic is also highly<br />
relevant to the tragic sudden infant<br />
death (SID) syndrome. Further studies<br />
are in progress to investigate this<br />
issue.<br />
34<br />
Finally, the twin studies have been<br />
helpful in identifying a new candidate<br />
gene for FCHL. We first looked for<br />
linkage between the loci for the<br />
peroxisome proliferator-activating<br />
protein receptor (PPAR) γ gene and its<br />
binding partner, the retinoid X<br />
receptor (RXR) gene. The former<br />
gene is strongly implicated in the<br />
development of obesity. We found that<br />
the PPAR γ gene locus is linked to<br />
HDL cholesterol and body mass<br />
index. Furthermore, the RXR gene<br />
locus was strongly linked to<br />
triglycerides. Since RXR is located<br />
precisely at the chromosome 1q locus<br />
linked to FCHL, RXR immediately<br />
becomes a very attractive candidate<br />
gene for this condition.<br />
New perspectives<br />
Katrin Hoffmann is studying an<br />
isolated population in Germany,<br />
namely the Sorbs. She has collected<br />
60 families with hypertension and is<br />
in the process of performing a total<br />
genome scan in cooperation with<br />
André Reis. Tom Lindner, who has<br />
collected 350 sibpairs with type 2<br />
diabetes from eastern Germany, joins<br />
the group after a fellowship with<br />
Graeme Bell at the University of<br />
Chicago. He is funded to conduct<br />
family studies involving a cohort of<br />
dialysis patients with type 2 diabetes.<br />
5,0<br />
4,0<br />
3,0<br />
2,0<br />
1,0<br />
0,0<br />
-1,0<br />
-2,0<br />
-3,0<br />
D13S175<br />
LOD<br />
D13S217<br />
D13S171<br />
D13S263<br />
D13S153<br />
D13S1306 D13S789<br />
D13S156<br />
D13S795 D13S1300<br />
D13S794<br />
D13S265<br />
D13S170 D13S271<br />
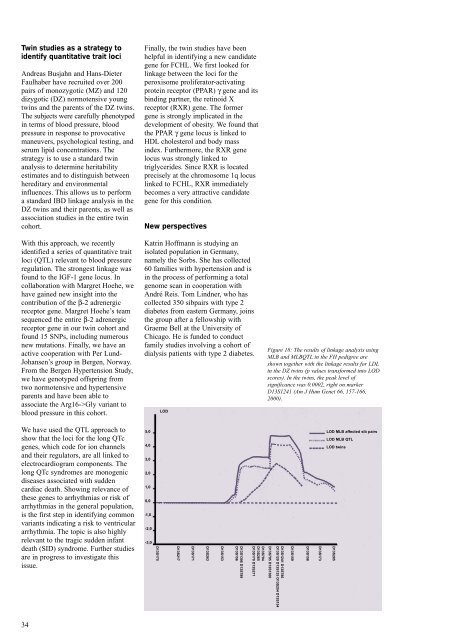
Figure 18: The results of linkage analysis using<br />
MLB and MLBQTL in the FH pedigree are<br />
shown together with the linkage results for LDL<br />
in the DZ twins (p values transformed into LOD<br />
scores). In the twins, the peak level of<br />
significance was 0.0002, right on marker<br />
D13S1241 (Am J Hum Genet 66, 157-166,<br />
<strong>2000</strong>).<br />
D13S1241 D13S786<br />
D13S129 D13S125 D13S254 D13S154<br />
D13S159<br />
D13S158<br />
D13S173<br />
LOD MLB affected sib pairs<br />
LOD MLB QTL<br />
LOD twins<br />
D13S285