You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Coupling of Gab1 to c-Met, Grb2<br />
and downstream effectors<br />
mediate biological responses<br />
Ute Schaeper, Martin Sachs, Niels<br />
H. Gehring, Renate Franke and<br />
Ingrid Walther. In collaboration with<br />
Bettina Kemkes (GSF Munich) and<br />
Carmen Birchmeier (<strong>MDC</strong>)<br />
Gab1, like the insulin receptor<br />
substrates (IRS), the FGF receptor<br />
substrate FRS/SNT, and p62dok<br />
family members belongs to a newly<br />
identified group of docking proteins<br />
that function as specific substrates of<br />
tyrosine kinases. Gab1 contains an Nterminal<br />
PH domain and a novel<br />
phosphotyrosine recognition domain<br />
which mediate direct association with<br />
the c-Met receptor. Gab1 binds to two<br />
sites of the cytoplasmic tail of c-Met,<br />
Y14 (Y1349) and to a lesser extent<br />
Y15 (Y1356). Gab1 also forms a<br />
constitutive complex with Grb2 and<br />
this interaction is mediated via the<br />
C-terminal SH3 domain of Grb2.<br />
76<br />
We have now mapped the c-Met and<br />
Grb2 interaction sites using reverse<br />
yeast two-hybrid technology. The c-<br />
Met binding site is localized to a 13<br />
amino acid region unique to Gab1.<br />
Insertion of this site into the Gab1related<br />
protein p97/Gab2 was<br />
sufficient to confer c-Met binding<br />
activity. Association with Grb2 was<br />
mapped to two sites: a classical SH3<br />
binding site (PXXP) and a novel Grb2<br />
SH3 consensus binding motif<br />
(PP(V/I)(D/N)RXXKP). To detect<br />
phosphorylation-dependent<br />
interactions of Gab1 with downstream<br />
substrates, we have developed a<br />
modified yeast two-hybrid assay and<br />
identified PI(3)K, Shc, Shp2 and<br />
CRKL as interaction partners of Gab1.<br />
In a trk-met specific branching<br />
morphogenesis assay, association of<br />
Gab1 with Shp2, but not PI(3)K,<br />
CRKL or Shc was essential to induce<br />
branching morphogenesis in <strong>MDC</strong>K<br />
cells. A fundamental role of Gab1 for<br />
c-Met specific signaling is also<br />
supported by gene ablation<br />
experiments in the mouse: Gab1 -/embryos<br />
produced in our laboratory<br />
are characterized by strongly reduced<br />
and delayed migration of myogenic<br />
precursor cells into the limbs, a<br />
phenotype reminiscent of HGF/SF -/and<br />
c-Met -/- mutant embryos.<br />
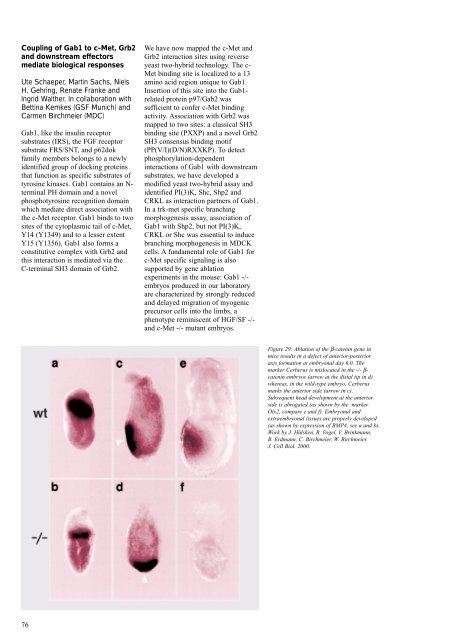
Figure 29: Ablation of the β-catenin gene in<br />
mice results in a defect of anterior-posterior<br />
axis formation at embryonal day 6.0. The<br />
marker Cerberus is mislocated in the -/- βcatenin<br />
embryos (arrow at the distal tip in d)<br />
whereas, in the wild-type embryo, Cerberus<br />
marks the anterior side (arrow in c).<br />
Subsequent head development at the anterior<br />
side is abrogated (as shown by the marker<br />
Otx2, compare e and f). Embryonal and<br />
extraembryonal tissues are properly developed<br />
(as shown by expression of BMP4, see a and b).<br />
Work by J. Hülsken, R. Vogel, V. Brinkmann,<br />
B. Erdmann, C. Birchmeier, W. Birchmeier.<br />
J. Cell Biol. <strong>2000</strong>.