Caché System Administration Guide - InterSystems Documentation
Caché System Administration Guide - InterSystems Documentation
Caché System Administration Guide - InterSystems Documentation
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
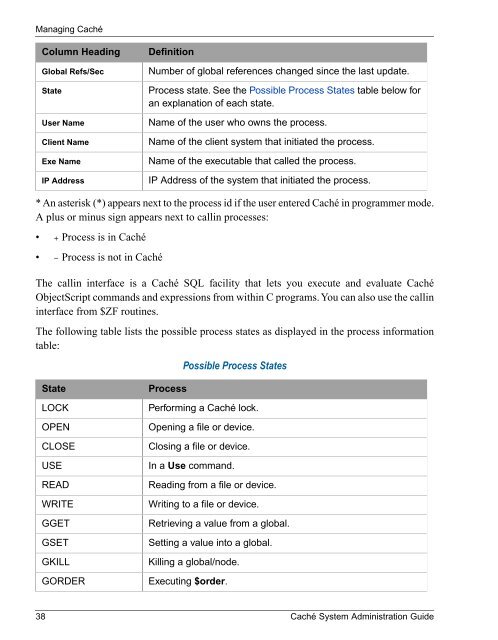
Managing <strong>Caché</strong>Column HeadingGlobal Refs/SecStateUser NameClient NameExe NameIP AddressDefinitionNumber of global references changed since the last update.Process state. See the Possible Process States table below foran explanation of each state.Name of the user who owns the process.Name of the client system that initiated the process.Name of the executable that called the process.IP Address of the system that initiated the process.* An asterisk (*) appears next to the process id if the user entered <strong>Caché</strong> in programmer mode.A plus or minus sign appears next to callin processes:• + Process is in <strong>Caché</strong>• – Process is not in <strong>Caché</strong>The callin interface is a <strong>Caché</strong> SQL facility that lets you execute and evaluate <strong>Caché</strong>ObjectScript commands and expressions from within C programs. You can also use the callininterface from $ZF routines.The following table lists the possible process states as displayed in the process informationtable:Possible Process StatesStateLOCKOPENCLOSEUSEREADWRITEGGETGSETGKILLGORDERProcessPerforming a <strong>Caché</strong> lock.Opening a file or device.Closing a file or device.In a Use command.Reading from a file or device.Writing to a file or device.Retrieving a value from a global.Setting a value into a global.Killing a global/node.Executing $order.38 <strong>Caché</strong> <strong>System</strong> <strong>Administration</strong> <strong>Guide</strong>