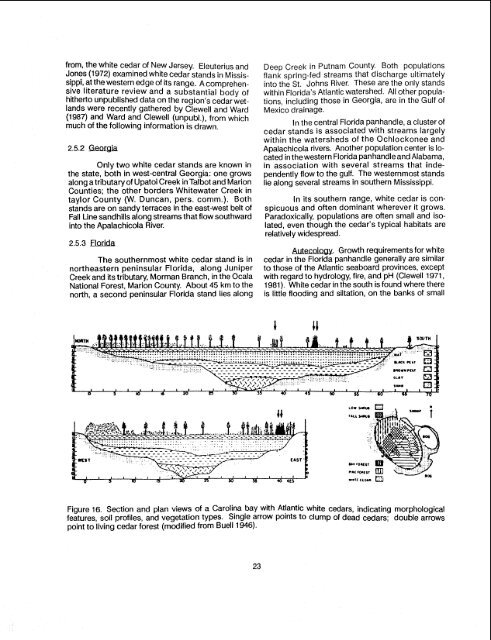
tablished. Drainage from 224 krn <strong>of</strong> ditches and thesoil compaction and damming effect <strong>of</strong> 252 krn <strong>of</strong>roads, exacerbated by accelerating rates <strong>of</strong>upstream run<strong>of</strong>f, have seriously lowered the watertable in many areas and impounded and floodedothers. <strong>The</strong> net effect has been to progressivelyreplace the distinctive cypress and <strong>Atlantic</strong> <strong>white</strong><strong>cedar</strong> communities by a relatively uniform red mapleblackgum forest. An extensive master plan wasdeveloped by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service(USFWS 1986b) in an effort to reverse this trend. Keyaspects <strong>of</strong> the proposed management program (inreview at the time <strong>of</strong> this writing) are outlined in Chapter6.2.4.2 South CarolinaInformation on South Carolina <strong>cedar</strong> <strong>wetlands</strong>flora and its distribution was provided by J. Nelson(pers. comm.) and D.A. Rayner (pers. comm.).Early records <strong>of</strong> the botanical and logging history <strong>of</strong>North and South Carolina are described by Frost(1 987 and unpubl.) (Figure 14).Radford (1 976) lists five counties in SouthCarolina having populations <strong>of</strong> <strong>white</strong> <strong>cedar</strong>: Lexington,Kershaw, Chesterfield, Darlington, andMarlboro. Populations are also known from Horry,Geor~etown, Richland, and Sumter Counties, and itis very likely that <strong>white</strong> <strong>cedar</strong> is also present in AikenCounty. All but two <strong>of</strong> these counties are part <strong>of</strong> themidlands <strong>of</strong> South Carolina, where extensiveacreages <strong>of</strong> xeric sandhills are associated withpalustrine communities. Francis Marion <strong>National</strong>Forest contains a few small <strong>cedar</strong> stands.<strong>The</strong> South Carolina HeritageTrust data baseplaces Chamaecyparis habitats within the 'RtlanticWhite Cedar Bog" community. All the sites foundwithin sandhill areas are quite similar (J. Nelson, pers.comm.). <strong>The</strong>y always seem to be associated withcreek drainages and may extend for several milesnear the base <strong>of</strong> a slope at the creek edge. White<strong>cedar</strong> forms dense forest at times and sometimesmoves onto the sides <strong>of</strong> the adjacent hills, especiallyif there is a hardpan <strong>of</strong> ironstone near the top that forceswater out along the slopes as intermittentseepages. <strong>The</strong> water within the sandhill creeks iseither clear or tea-colored: its color appears to be relatedto the size <strong>of</strong> the stream itself and the distanceit has flowed from its headwaters.In very wet areas, abundant Sphagnum isfound with lady's slipper (Cyprepedium acaule), cinnamonfern (Osmunda cinnamomea), and sedges(especially Rhynchospora spp.). Golden club (Orontiumaquaticum), tuckahoe (Peltandra virginica), andpitcher plant (Sarracenia rubra) are also found.Shrubs in these bogs usually include fetterbush(Lyonia lucida), gallberries (Ilex spp.), blueberries(Vaccinium sp p.) , titi (Cyrilla racemiflora), andgreen brier (Smilax lsaurjfolia). Vaccinium sempervirens,a law shrub thought to be endemic to someLexington Carolina bays are a wetland type <strong>of</strong> unknownorigin primarily restricted to North and SouthCarolina. <strong>The</strong> bays, dominated by evergreen shrubs,form elongated elliptical depressions on a northwest,southeast axis (Richardson 1981).County drainages, co-occurs with <strong>Atlantic</strong><strong>white</strong> <strong>cedar</strong> (Rayner and Henderson 1980). Redmaple, red bay, loblolly bay (Gordonia lasianthus),sweet bay, and black gum are frequently seen treespecies which sometimes occur as large, branchedshrubs. Pond pine is occasionally present. Ingeneral, these bogs tend to have essentially thesame sort <strong>of</strong> vegetation as many <strong>of</strong> the pocosin sitesin South Carolina, but with a higher and thickercanopy, and perhaps a less diverse shrub layer.An unusual <strong>white</strong> <strong>cedar</strong> wetland, with a differentsuite <strong>of</strong> species, is found in Sumter County.<strong>The</strong>re is also at least one large Carolina bay in SouthCarolina (on the bombing range <strong>of</strong> an Air Force base)containing large <strong>white</strong> <strong>cedar</strong>s. Carolina bays are awetland type <strong>of</strong> unknown origin primarilyrestricted toNorth and South Carolina. <strong>The</strong> bays, dominated byevergreen shrubs, form elongated elliptical depressionson a northwest, southeast axis (Richardson1981). A cross section through a Carolina bay withChamaecyparis is shown in Figure 16.2.5 JUNIPER SWAMPS OF THE SOUTHEAST<strong>Atlantic</strong> <strong>white</strong> <strong>cedar</strong> reaches its southernmostdistributional limits in Florida and along thegulf coast <strong>of</strong> Alabama and Mississippi (Figure 17).<strong>The</strong> <strong>cedar</strong> <strong>of</strong> Mississippi, Alabama, and westernFlorida differs in some vegetative and reproductivecharacters from that in eastern Florida anorthward. Although controversy surroundstaxonomy (A. Gholson, pers. comm.; Li 1962),accepted designation is C. thyoides var. henryaeLittle 1966). Literature on <strong>Atlantic</strong> <strong>white</strong> <strong>cedar</strong> inFlorida and along the gulf coast is sparse. W(1963) and Collins et al. (1964) briefly describedtwo southernmost stands <strong>of</strong> the species, whichboth in peninsular Florida. Despite the fact thatlargest <strong>cedar</strong> living today grows in AlabSection 3.2.41, as <strong>of</strong> this writing scientific fite<strong>Atlantic</strong> <strong>white</strong> <strong>cedar</strong> in that state is virtuallistent. In 1791, Williamdescribed strange <strong>cedar</strong>s growing along tbia River, noting their similarity to, and differe
from, the <strong>white</strong> <strong>cedar</strong> <strong>of</strong> New Jersey. Eleuterius andJones (1972) examined <strong>white</strong> <strong>cedar</strong> stands in Mississippi,at the western edge <strong>of</strong> its range. A comprehensiveliterature review and a substantial body <strong>of</strong>hitherto unpublished data on the region's <strong>cedar</strong> <strong>wetlands</strong>were recently gathered by Clewell and Ward(1987) and Ward and Clewell (unpubl.), from whichmuch <strong>of</strong> the following information is drawn.Only two <strong>white</strong> <strong>cedar</strong> stands are known inthe state, both in west-central Georgia: one growsalong a tributary <strong>of</strong> Upatoi Creek in Talbot and MarionCounties; the other borders Whitewater Creek intayior County (W. Duncan, pers. comrn.). Bothstands are on sandy terraces in the east-west belt <strong>of</strong>Fall Line sandhills along streams that flow southwardinto the Apalachicola River.2.5.3 Florida<strong>The</strong> southernmost <strong>white</strong> <strong>cedar</strong> stand is innortheastern peninsular Florida, along JuniperCreek and its tributary, Morman Branch, in the Ocala<strong>National</strong> Forest, Marion County. About 45 km to thenorth, a second peninsular Florida stand lies alongDeep Creek in Putnam County. Both populationsflank spring-fed streams that discharge ultimatelyinto the St. Johns River. <strong>The</strong>se are the only standswithin Florida's Atfantic watershed. All other populations,including those in Georgia, are in the Gulf <strong>of</strong>Mexico drainage.In the central Florida panhandle, a cluster <strong>of</strong><strong>cedar</strong> stands is associated with streams largelywithin the watersheds <strong>of</strong> the Ochlockonee andApalachicola rivers. Another population center is locatedin the western Florida panhandle and Alabama,in association with several streams that independentlyflow to the gulf. <strong>The</strong> westernmost standslie along several streams in southern Mississippi.In its southern range, <strong>white</strong> <strong>cedar</strong> is conspicuousand <strong>of</strong>ten dominant wherever it grows.Paradoxically, populations are <strong>of</strong>ten small and isolated,even though the <strong>cedar</strong>'s typical habitats arerelatively widespread.m. Growth requirements for <strong>white</strong><strong>cedar</strong> in the Florida panhandle generally are similarto those <strong>of</strong> the <strong>Atlantic</strong> seaboard provinces, exceptwith regard to hydrology, fire, and pH (Clewell 1971,1981). White <strong>cedar</strong> in the south is found where thereis little flooding and siltation, on the banks <strong>of</strong> smallFigure 16. Section and plan views <strong>of</strong> a Carolina bay with <strong>Atlantic</strong> <strong>white</strong> <strong>cedar</strong>s, indicating morphologicalfeatures, soil pr<strong>of</strong>iles, and vegetation types. Single arrow points to clump <strong>of</strong> dead <strong>cedar</strong>s; double arrowspoint to living <strong>cedar</strong> forest (modified from Buell 1946).
- Page 1: Biological Report 85(7.21)July 1989
- Page 5 and 6: PREFACEThis monograph on the ecolog
- Page 7 and 8: CONTENTSea9tl.PREFACE .............
- Page 9 and 10: NumberTABLESEarliest records of Atl
- Page 11 and 12: - CHAPTER 1 -INTRODUCTION1 .I GENER
- Page 13 and 14: TEMPORARLYSEASONALLY1I SATURATED1Fi
- Page 15 and 16: Stagnant,,- melting Icel Block d~ag
- Page 17: Table I. Earliest records of Atlant
- Page 20 and 21: CHAPTER 2 -REGIONAL OVERVIEW2.1 INT
- Page 22 and 23: stands are scattered north and west
- Page 24 and 25: state and is gathering data hithert
- Page 26 and 27: corner of the state, and Uttertown
- Page 28 and 29: hardwood stands, or as isolated tre
- Page 30 and 31: cedar have comprised 40%-60% of the
- Page 34 and 35: perennial streams (Figure 18) and i
- Page 36 and 37: - CHAPTER 3 -CHAMAECYPARIS THYOIDES
- Page 38 and 39: Ms&gua As early as 1923, Akermandes
- Page 40 and 41: - CHAPTER 4 -STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
- Page 42 and 43: ottomland-isolatedtill & bedrockupl
- Page 44 and 45: Table 5. Mean August tissue nutrien
- Page 46 and 47: - CHAPTER 5 -BIOLOGICAL COMPONENTS
- Page 48 and 49: Figure 24a. Companions: plants freq
- Page 50 and 51: Figure 24c. Companions: Plants freq
- Page 52 and 53: ?able 7. Comparison of bird species
- Page 54 and 55: Meanley (1979) emphasized the impor
- Page 56 and 57: - CHAPTER 6 -MANAGEMENT AND HARVEST
- Page 58 and 59: FireBurnedtreesPeatGlacialrubble-Tr
- Page 60 and 61: Mixedhardwood& shrubsPeatGlacialrub
- Page 62 and 63: acidity is reduced, and ammonia, ph
- Page 64 and 65: and condition of the soil surface a
- Page 66 and 67: sprouts and shade-tolerant shrubs g
- Page 68 and 69: Figure 32. Atlantic white cedar reg
- Page 70 and 71: sedhflings, conversely, canopy open
- Page 72 and 73: FORESTMANAGEMENTSCHEMAT I CLEGEND-
- Page 74 and 75: -.- Rsfupe BoundaryState BoundaryRo
- Page 76 and 77: NATIONAL WILDLIFE RERX;EVirginia an
- Page 78 and 79: Figure 38. Alligator River (North C
- Page 80 and 81: Mainland Dare County is located on
- Page 82 and 83:
The cedar swamp forests along the A
- Page 84 and 85:
IPure Atlanticwhite cedar standsy-J
- Page 86 and 87:
Generally, the mixed swamp forest s
- Page 88 and 89:
species of mammals are recorded by
- Page 90 and 91:
Braun-Blanquet, J. [I 9321 1983. Pl
- Page 92 and 93:
Ferguson, R.H., and C.E. Meyer. 197
- Page 94 and 95:
Littte, S. 1953. Prescribed burning
- Page 96 and 97:
Porter, D.M. 1979. Rare and endange
- Page 98 and 99:
Gov. Print. Off., Washington, DC. (
- Page 101 and 102:
APPENDIX A. Flora Associated with C
- Page 103 and 104:
APPENDIX A. Flora: Trees (6ontin~ed
- Page 106 and 107:
APPENDIX A. Flora: Shrubs (Continue
- Page 108 and 109:
APPENDIX A. Fiora: Herbs (Continud)
- Page 110 and 111:
APPENDIX A. Flora: Herbs (Continued
- Page 112 and 113:
APPENDIX A. flora: Herbs (Continued
- Page 114 and 115:
APPENDIX A. Flora: Herbs (Continued
- Page 116 and 117:
APPENDIX A. Flora: Herbs (Continued
- Page 118 and 119:
APPENDIX B. FAUNA OF ATLANTIC WHITE
- Page 120 and 121:
APPENDIX C. Hydric Soilsis a soil t
- Page 122 and 123:
Frost, CecilFuller, ManleyFunk, Dav
- Page 124 and 125:
Ward, Daniel B.Whigham, DennisWidof