Introduction to Krylov subspace methods - IMAGe
Introduction to Krylov subspace methods - IMAGe
Introduction to Krylov subspace methods - IMAGe
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
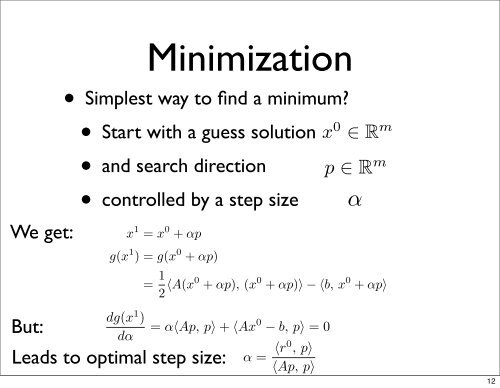
jx j − b kMinimizationjm∑•j=1Simplest way <strong>to</strong> find j=1 a minimum?∇g = Ax − b = 0 ⇐⇒•∇g = Ax − b = 0 ⇐⇒ AxStart with a guess ∗ Ax ∗ = b,= b,solution• and search directionx 1 = x 0 + αp• controlled g(x 1 ) = g(x 0 by + αp) a step sizej=1∴ (∇g) k ∑ j − b k= 1 ∑= ∴ 1 (∇g) a kja kj x j + 1 x∑j + 1 2 k = aa2kj x ja ik −xb ik− b kj2 j=1 ∇g 2 = Axik xi− bj=1bk= 0 ⇐⇒ Ax ∗ = b,Ax − b = 0 ⇐⇒ It means Ax ∗ = that ∴ b, (∇g) the xm∑∗ k = : solution solution a kj x j −of bof k Ax Ax = = b is b also thx ∗ : solution of Ax = bolutionNow, what’sof Axthe=best Now, b isand also what’s simplestthemethod minimum best <strong>to</strong> and of g. simplest methodx ∗ xfind ∗ : solutiona minimum?of Ax = beminimum Starting with a ”guess”best and simplest of Starting g.x 0 ∈ Rmethod with m and a non-zero: solutionvec<strong>to</strong>ra <strong>to</strong> ”guess” find axminimum?0 ofp ∈Ax∈ R R m =withbstep lengthand a non-zeItdetermined It meansmeans thatin thatthe a solution waythe<strong>to</strong>solutionminimizeof Ax = b is also the of g.of Ax = b is also the minimum of g.<strong>to</strong> ess” find Now,Now,x 0 what’s ∈a what’sRminimum?the m determined besttheand andbesta simplestand simplestnon-zeroinmethod a way methodvec<strong>to</strong>r find<strong>to</strong> minimizeafindpminimum?a minimum?∈ R m with step leny <strong>to</strong> minimizeodetermined vec<strong>to</strong>r determined pa way in ∈a R<strong>to</strong> way minimizem <strong>to</strong>with minimizestep length αWex 1 get:= x 0 + αpx 1 ) = g(x 0 + αp)2 i,j2∑ m∑ i,j ∑ i=1∇g = Ax − b = 0 ⇐⇒ Ax ∗ = b,It means that the solution∴ of (∇g) Ax = k b=is also a kj the x j −minimum b k of g.StartingStartingwithwitha ”guess”a ”guess”x 0 ∈ Rx 0 m ∈andR m aandnon-zeroa non-zerovec<strong>to</strong>rvec<strong>to</strong>rp ∈ R m pwith∈ R m stepwithlengthstepαlengx 1 = x 0 + αpg(x 1 ) = g(x 0 + αp)= 1 2 〈A(x0 + αp), (x 0 += 1 2 〈A(x0 dg(x 1 dg(x ) + 1 αp), (x 0 dg(x αp)〉 1 )− 〈b, x 0 + αp〉dα= α〈Ap, )But:p〉 + 〈Ax0 − b, p〉 =dα = 0 and α〈Ap, then we p〉 find + ”α”dα= α〈Ap, p〉 + 〈Ax0 〈Ap, − b, p〉 p〉 = 0 and then we find ”α”〈Ax0 − b, p〉Leads <strong>to</strong> optimal step size: ∴ α = 〈r0 , p〉ix 1 = x= 1 1 0 + = αp x 0 + αp2 〈A(x0 + αp), (x 0 + αp)〉 − 〈b, x 0 + αp〉g(x 1 ) g(x = g(x 1 ) = 0 + g(x αp)0 + αp)dg(x 1 )dα= = α〈Ap, 1 2 〈A(x0 = p〉 1 + αp), (x 0 + αp)〉 − 〈b, x 0 + αp〉2 〈A(x0 〈Ax0 − b, p〉+ αp), (x 0 = 0 and then we+ αp)〉 − 〈b, x 0 find ”α”+ αp〉α = −〈Ax0 − b, p〉p)〉 − 〈b, x 0 α = −〈Ax0 − b, p〉α = −〈Ax0 − b, p〉+ αp〉 0〈Ap, p〉〈Ap, p〉〈Ap, p〉x ∗ : solution of Ax = b012