Introduction to Krylov subspace methods - IMAGe
Introduction to Krylov subspace methods - IMAGe
Introduction to Krylov subspace methods - IMAGe
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
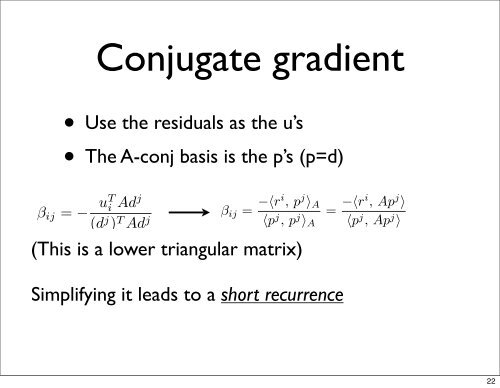
j 〉 = 〈u i +∴= u i Ad +Conjugate gradient∑i−1β ik d k , Ad j 〉k=0= u T i Ad j +• Use the β ik (dresiduals k ) T Ad j as the u’s•Suppose k=0 u i = r i (cheap!)The A-conj basis is the p’s (p=d)∴k=0β ik (d ) Ad= u T i Ad j + β ij (d j ) T Ad j = 0β ij = − uT i Adj(d j ) T Ad jThis is not cheap, since we need <strong>to</strong> keep the vec<strong>to</strong>rs ”d” <strong>to</strong> solve the∑i−1= u T i Ad j + β ij (d j ) T Ad j = 0β ij = − uT i Adj(d j ) T Ad jp i = d i(This is a lower triangular matrix)(A-conj. GS)β ij = −〈ri , p j 〉 A〈p j , p j 〉 A= −〈ri , Ap j 〉〈p j , Ap j 〉 .e need <strong>to</strong> keep the vec<strong>to</strong>rs ”d” <strong>to</strong> solve the problem.From x i+1 = x i + α i p i : r i+1 = r i − α i Ap id i〈r j+1 , r i 〉 = 〈r j , r i 〉 − α j 〈Ap j , r i 〉Simplifying it leads <strong>to</strong> a short recurrence(A-conj. GS)−〈r i , p j 〉 A〈p j , p j 〉 A= −〈ri , Ap j 〉〈p j , Ap j 〉 .α j 〈Ap j , r i 〉 = 〈r j , r i 〉 − 〈r j+1 , r i 〉α j β ij 〈Ap j , p j 〉 = 〈r j+1 , r i 〉 − 〈r j , r i 〉∴ β ij = 〈ri , r j+1 〉α j 〈Ap j , p j 〉 − 〈rj , r i 〉α j 〈Ap j , p j 〉22