Annual Report 2011 - Center for Advanced Biotechnology and ...
Annual Report 2011 - Center for Advanced Biotechnology and ...
Annual Report 2011 - Center for Advanced Biotechnology and ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
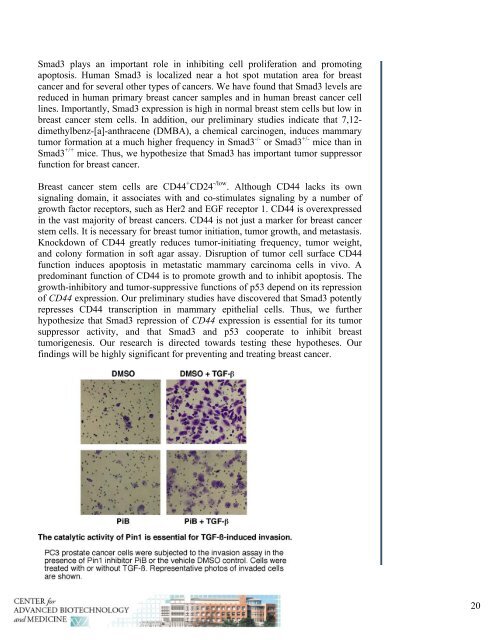
Smad3 plays an important role in inhibiting cell proliferation <strong>and</strong> promoting<br />
apoptosis. Human Smad3 is localized near a hot spot mutation area <strong>for</strong> breast<br />
cancer <strong>and</strong> <strong>for</strong> several other types of cancers. We have found that Smad3 levels are<br />
reduced in human primary breast cancer samples <strong>and</strong> in human breast cancer cell<br />
lines. Importantly, Smad3 expression is high in normal breast stem cells but low in<br />
breast cancer stem cells. In addition, our preliminary studies indicate that 7,12dimethylbenz-[a]-anthracene<br />
(DMBA), a chemical carcinogen, induces mammary<br />
tumor <strong>for</strong>mation at a much higher frequency in Smad3 -/- or Smad3 +/- mice than in<br />
Smad3 +/+ mice. Thus, we hypothesize that Smad3 has important tumor suppressor<br />
function <strong>for</strong> breast cancer.<br />
Breast cancer stem cells are CD44 + CD24 -/low . Although CD44 lacks its own<br />
signaling domain, it associates with <strong>and</strong> co-stimulates signaling by a number of<br />
growth factor receptors, such as Her2 <strong>and</strong> EGF receptor 1. CD44 is overexpressed<br />
in the vast majority of breast cancers. CD44 is not just a marker <strong>for</strong> breast cancer<br />
stem cells. It is necessary <strong>for</strong> breast tumor initiation, tumor growth, <strong>and</strong> metastasis.<br />
Knockdown of CD44 greatly reduces tumor-initiating frequency, tumor weight,<br />
<strong>and</strong> colony <strong>for</strong>mation in soft agar assay. Disruption of tumor cell surface CD44<br />
function induces apoptosis in metastatic mammary carcinoma cells in vivo. A<br />
predominant function of CD44 is to promote growth <strong>and</strong> to inhibit apoptosis. The<br />
growth-inhibitory <strong>and</strong> tumor-suppressive functions of p53 depend on its repression<br />
of CD44 expression. Our preliminary studies have discovered that Smad3 potently<br />
represses CD44 transcription in mammary epithelial cells. Thus, we further<br />
hypothesize that Smad3 repression of CD44 expression is essential <strong>for</strong> its tumor<br />
suppressor activity, <strong>and</strong> that Smad3 <strong>and</strong> p53 cooperate to inhibit breast<br />
tumorigenesis. Our research is directed towards testing these hypotheses. Our<br />
findings will be highly significant <strong>for</strong> preventing <strong>and</strong> treating breast cancer.<br />
20