acta 2_2015
acta 2_2015
acta 2_2015
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
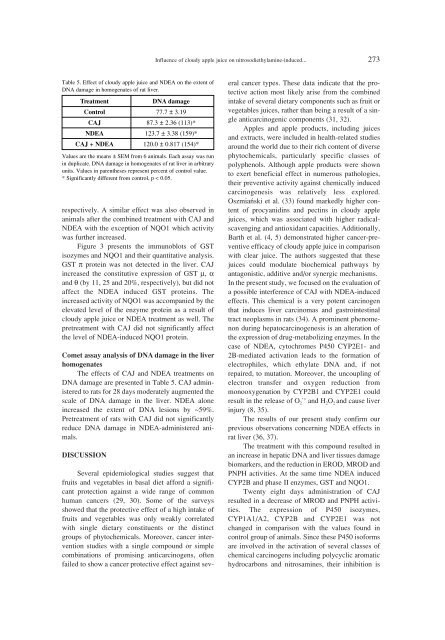
Influence of cloudy apple juice on nitrosodiethylamine-induced... 273Table 5. Effect of cloudy apple juice and NDEA on the extent ofDNA damage in homogenates of rat liver.TreatmentDNA damageControl 77.7 ± 3.19CAJ 87.3 ± 2.36 (113)*NDEA 123.7 ± 3.38 (159)*CAJ + NDEA 120.0 ± 0.817 (154)*Values are the means ± SEM from 6 animals. Each assay was runin duplicate. DNA damage in homogenates of rat liver in arbitraryunits. Values in parentheses represent percent of control value.* Significantly different from control, p < 0.05.respectively. A similar effect was also observed inanimals after the combined treatment with CAJ andNDEA with the exception of NQO1 which activitywas further increased.Figure 3 presents the immunoblots of GSTisozymes and NQO1 and their quantitative analysis.GST π protein was not detected in the liver. CAJincreased the constitutive expression of GST µ, αand θ (by 11, 25 and 20%, respectively), but did notaffect the NDEA induced GST proteins. Theincreased activity of NQO1 was accompanied by theelevated level of the enzyme protein as a result ofcloudy apple juice or NDEA treatment as well. Thepretreatment with CAJ did not significantly affectthe level of NDEA-induced NQO1 protein.Comet assay analysis of DNA damage in the liverhomogenatesThe effects of CAJ and NDEA treatments onDNA damage are presented in Table 5. CAJ administeredto rats for 28 days moderately augmented thescale of DNA damage in the liver. NDEA aloneincreased the extent of DNA lesions by ~59%.Pretreatment of rats with CAJ did not significantlyreduce DNA damage in NDEA-administered animals.DISCUSSIONSeveral epidemiological studies suggest thatfruits and vegetables in basal diet afford a significantprotection against a wide range of commonhuman cancers (29, 30). Some of the surveysshowed that the protective effect of a high intake offruits and vegetables was only weakly correlatedwith single dietary constituents or the distinctgroups of phytochemicals. Moreover, cancer interventionstudies with a single compound or simplecombinations of promising anticarcinogens, oftenfailed to show a cancer protective effect against severalcancer types. These data indicate that the protectiveaction most likely arise from the combinedintake of several dietary components such as fruit orvegetables juices, rather than being a result of a singleanticarcinogenic components (31, 32).Apples and apple products, including juicesand extracts, were included in health-related studiesaround the world due to their rich content of diversephytochemicals, particularly specific classes ofpolyphenols. Although apple products were shownto exert beneficial effect in numerous pathologies,their preventive activity against chemically inducedcarcinogenesis was relatively less explored.OszmiaÒski et al. (33) found markedly higher contentof procyanidins and pectins in cloudy applejuices, which was associated with higher radicalscavengingand antioxidant capacities. Additionally,Barth et al. (4, 5) demonstrated higher cancer-preventiveefficacy of cloudy apple juice in comparisonwith clear juice. The authors suggested that thesejuices could modulate biochemical pathways byantagonistic, additive and/or synergic mechanisms.In the present study, we focused on the evaluation ofa possible interference of CAJ with NDEA-inducedeffects. This chemical is a very potent carcinogenthat induces liver carcinomas and gastrointestinaltract neoplasms in rats (34). A prominent phenomenonduring hepatocarcinogenesis is an alteration ofthe expression of drug-metabolizing enzymes. In thecase of NDEA, cytochromes P450 CYP2E1- and2B-mediated activation leads to the formation ofelectrophiles, which ethylate DNA and, if notrepaired, to mutation. Moreover, the uncoupling ofelectron transfer and oxygen reduction frommonooxygenation by CYP2B1 and CYP2E1 couldresult in the release of O 2∑- and H2 O 2 and cause liverinjury (8, 35).The results of our present study confirm ourprevious observations concerning NDEA effects inrat liver (36, 37).The treatment with this compound resulted inan increase in hepatic DNA and liver tissues damagebiomarkers, and the reduction in EROD, MROD andPNPH activities. At the same time NDEA inducedCYP2B and phase II enzymes, GST and NQO1.Twenty eight days administration of CAJresulted in a decrease of MROD and PNPH activities.The expression of P450 isozymes,CYP1A1/A2, CYP2B and CYP2E1 was notchanged in comparison with the values found incontrol group of animals. Since these P450 isoformsare involved in the activation of several classes ofchemical carcinogens including polycyclic aromatichydrocarbons and nitrosamines, their inhibition is