Determination of Creep Compliance and Tensile Strength of Hot-Mix ...
Determination of Creep Compliance and Tensile Strength of Hot-Mix ...
Determination of Creep Compliance and Tensile Strength of Hot-Mix ...
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
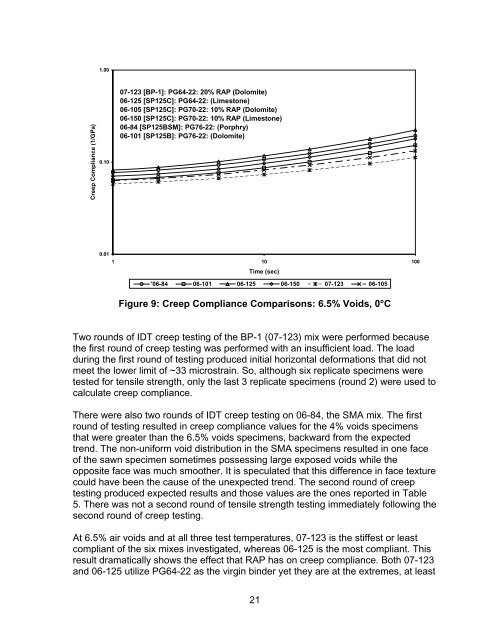
1.00<strong>Creep</strong> <strong>Compliance</strong> (1/GPa)0.1007-123 [BP-1]: PG64-22: 20% RAP (Dolomite)06-125 [SP125C]: PG64-22: (Limestone)06-105 [SP125C]: PG70-22: 10% RAP (Dolomite)06-150 [SP125C]: PG70-22: 10% RAP (Limestone)06-84 [SP125BSM]: PG76-22: (Porphry)06-101 [SP125B]: PG76-22: (Dolomite)0.011 10 100Time (sec)'06-84 06-101 06-125 06-150 07-123 06-105Figure 9: <strong>Creep</strong> <strong>Compliance</strong> Comparisons: 6.5% Voids, 0°CTwo rounds <strong>of</strong> IDT creep testing <strong>of</strong> the BP-1 (07-123) mix were performed becausethe first round <strong>of</strong> creep testing was performed with an insufficient load. The loadduring the first round <strong>of</strong> testing produced initial horizontal deformations that did notmeet the lower limit <strong>of</strong> ~33 microstrain. So, although six replicate specimens weretested for tensile strength, only the last 3 replicate specimens (round 2) were used tocalculate creep compliance.There were also two rounds <strong>of</strong> IDT creep testing on 06-84, the SMA mix. The firstround <strong>of</strong> testing resulted in creep compliance values for the 4% voids specimensthat were greater than the 6.5% voids specimens, backward from the expectedtrend. The non-uniform void distribution in the SMA specimens resulted in one face<strong>of</strong> the sawn specimen sometimes possessing large exposed voids while theopposite face was much smoother. It is speculated that this difference in face texturecould have been the cause <strong>of</strong> the unexpected trend. The second round <strong>of</strong> creeptesting produced expected results <strong>and</strong> those values are the ones reported in Table5. There was not a second round <strong>of</strong> tensile strength testing immediately following thesecond round <strong>of</strong> creep testing.At 6.5% air voids <strong>and</strong> at all three test temperatures, 07-123 is the stiffest or leastcompliant <strong>of</strong> the six mixes investigated, whereas 06-125 is the most compliant. Thisresult dramatically shows the effect that RAP has on creep compliance. Both 07-123<strong>and</strong> 06-125 utilize PG64-22 as the virgin binder yet they are at the extremes, at least21