___________________________________________________________________________________________Disease EcologyOften with some common sense and a thorough knowledge of a field’s recent history, it is possible to findthe cause for specific plant symptoms. The following are guidelines that may be useful in diagnosingvegetable problems (modified from www6).Guidelines for diagnosing vegetable problems:1. Identify the symptoms. Do the leaves have a different color? Do leaves or the whole plant have adifferent appearance, e.g. smaller size leaves or bushy plants? Are there any leaf spots or spots onthe stems or fruits? Wilting of shoots or of the whole plant? Holes in the leaves or in the stem? Rootabnormalities? Fruit rot?2. Are all plants in the field affected? Are small areas in a field affected? Or individual plants?3. Determine if there is a pattern to the symptoms. Are affected plants growing in a low spot of thefield, poor drainage area, or an area with obviously compacted soil? Does the pattern correlate withcurrent field operations?4. Trace the problem’s history.• When were symptoms first noticed?• What rates of fertilizer and lime were used?• What pesticides were used?• What were the weather conditions like before you noticed the problems - cool or warm, wet ordry, windy, cloudy, sunny?5. Examine the plant carefully to determine if the problem may be caused by insects, diseases ormanagement practices.Insects: look for their presence or feeding signs on leaves, stems and roots. Sometimes it’s easierto find insects early in the morning or towards evening.Diseases: look for dead areas on roots, leaves, stems and flowers. Are the plants wilting eventhough soil moisture is plentiful? Then check the roots for root rot symptoms or root deformations.Are the leaves spotted or yellowed? Are there any signs of bacterial or fungal growth (soft rots,mildew, spores, etc.)? Look for virus symptoms: are the plants stunted or do they have obviousgrowth malformations? Are all the plants showing symptoms, or are just a few scattered around thefield?6. Could there be nutritional problems? The box below lists a number of characteristic deficiencysymptoms for the major and minor nutrients.7. Could there be a nutrient toxicity? Boron, zinc, and manganese may be a problem here. Soluble saltinjury may be seen as wilting of the plant even when the soil is wet. Burning of the leaf margins isusually from excessive fertilizer.8. Could soil problems be to blame? Soil problems such as compaction and poor drainage canseverely stunt plants.9. Could pesticide injury be at fault? <strong>Pest</strong>icide injury is usually uniform in the area or shows definitepatterns. Insecticides cause burning or stunting. Herbicides cause burning or abnormal growth.10. Could the damage be caused by environmental conditions? High or low temperatures, excessivelywet or dry, frost or wind damage, or even air pollution? Ozone levels may rise as hot, humid weathersettles in for long stretches. Look for irregularly shaped spots which may look similar to feeding ofmites and certain leafhoppers. Ozone flecks are usually concentrated in specific areas of the leaf,while feeding damage from insects is spread uniformly across the leaf.123<strong>Eggplant</strong> Ecological Guide
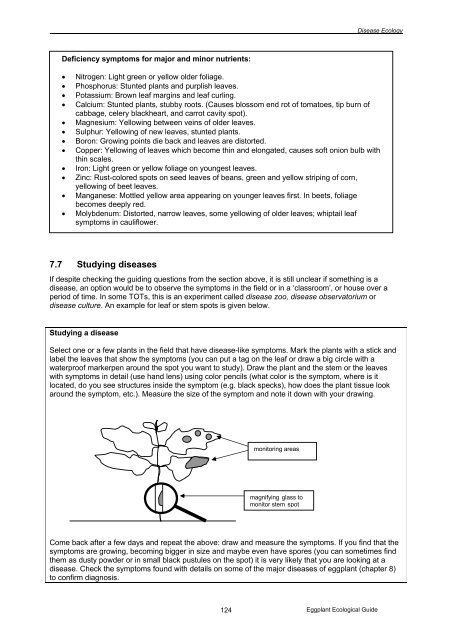
___________________________________________________________________________________________Disease EcologyDeficiency symptoms for major and minor nutrients:• Nitrogen: Light green or yellow older foliage.• Phosphorus: Stunted plants and purplish leaves.• Potassium: Brown leaf margins and leaf curling.• Calcium: Stunted plants, stubby roots. (Causes blossom end rot of tomatoes, tip burn ofcabbage, celery blackheart, and carrot cavity spot).• Magnesium: Yellowing between veins of older leaves.• Sulphur: Yellowing of new leaves, stunted plants.• Boron: Growing points die back and leaves are distorted.• Copper: Yellowing of leaves which become thin and elongated, causes soft onion bulb withthin scales.• Iron: Light green or yellow foliage on youngest leaves.• Zinc: Rust-colored spots on seed leaves of beans, green and yellow striping of corn,yellowing of beet leaves.• Manganese: Mottled yellow area appearing on younger leaves first. In beets, foliagebecomes deeply red.• Molybdenum: Distorted, narrow leaves, some yellowing of older leaves; whiptail leafsymptoms in cauliflower.7.7 Studying diseasesIf despite checking the guiding questions from the section above, it is still unclear if something is adisease, an option would be to observe the symptoms in the field or in a ‘classroom’, or house over aperiod of time. In some TOTs, this is an experiment called disease zoo, disease observatorium ordisease culture. An example for leaf or stem spots is given below.Studying a diseaseSelect one or a few plants in the field that have disease-like symptoms. Mark the plants with a stick andlabel the leaves that show the symptoms (you can put a tag on the leaf or draw a big circle with awaterproof markerpen around the spot you want to study). Draw the plant and the stem or the leaveswith symptoms in detail (use hand lens) using color pencils (what color is the symptom, where is itlocated, do you see structures inside the symptom (e.g. black specks), how does the plant tissue lookaround the symptom, etc.). Measure the size of the symptom and note it down with your drawing.monitoring areasmagnifying glass tomonitor stem spotCome back after a few days and repeat the above: draw and measure the symptoms. If you find that thesymptoms are growing, becoming bigger in size and maybe even have spores (you can sometimes findthem as dusty powder or in small black pustules on the spot) it is very likely that you are looking at adisease. Check the symptoms found with details on some of the major diseases of eggplant (chapter 8)to confirm diagnosis.124<strong>Eggplant</strong> Ecological Guide



![Section 4 [ PDF file, 252 KB] - The Field Alliance](https://img.yumpu.com/51387260/1/158x260/section-4-pdf-file-252-kb-the-field-alliance.jpg?quality=85)











