___________________________________________________________________________________Major Agronomic PracticesLime for control of soil-borne diseases?In some areas, lime is applied to the field for disease control. This has only been demonstrated forclubroot control in cabbage. However, lime may change the micro-environment in the soilsomewhat, resulting in changes of the population of micro-organisms, including pathogens. It mayalso have an effect on general crop health: by raising the pH, other nutrients become available,plants may grow better and stronger plants can resist diseases better. Set up an experiment to seewhat the effects of applying lime would be in your situation.In Hai Phong province, North Vietnam for example, farmers have tested the effects of applyingcompost (15 tons/ha) with and without crushed lime in the planting hole during transplanting ondisease occurrence in tomato. Results indicated that pest and blossom end rot incidence weresimilar in all treatments, but AESA led to pesticide applications being reduced from 11 in farmers’practice plots to 7 in the two IPM treatments. Yields were also higher by 37% and 50% fortreatments with and without lime, respectively. Profits increased from VND 558,000 in the farmers’practice treatment to VND 787,000 in the plus-lime IPM treatment, and VND 1,007,00 in the nolimeIPM treatment (pers. comm. Dr. J.Vos, 1999; and Vos, 2000, www16).3.7.7 Soil conservation and erosion controlMany farmers are concerned about how to keep or restore soil fertility in order to maintain good yields.Very often, the emphasis is on adding nutrients, not so much on protecting soil through soil conservation.Fertilization and soil conservation are actually equally important. Nutrients are linked with chemicalqualities of the soil, conservation also emphasizes the physical and biological characteristics of soil.Conservation is not only keeping soil parts where they are, but also keeping a good soil structure andstimulating the activity of micro-organisms in the soil.Some principles of soil conservation and fertilization (modified from Murakami, 1991):1. Keeping the soil covered.When soil is uncovered, it is easily attacked by rain, wind and sun heat. This is the main cause fordegradation of soil structure and soil erosion. During growth of a crop in the field, the soil can becovered by mulch (such as rice straw) or “living mulch” which is a crop that grows together with themain crop but is not harvested. When no production crop is planted in the field, consider sowing acover crop. This will keep the soil covered and thus protected from erosion by wind or water and it is avery good way of fertilizing the soil. See section 3.8.3.2. A cover crop can also be used as abiofumigation crop to sanitize the soil. See section 3.10.1.4.2. Regular supply of organic material to the soil.Adding organic material to soil is essential for good crop production! Organic matter such as compostcan supply all necessary nutrients to plants, and helps maintain a balanced pH. Organic matter alsostimulates activity of micro-organisms in the soil. Micro-organisms help releasing nutrients fromorganic material in the soil, help improve soil structure, and help protect roots from diseases. Seesection 3.8.3 on organic material.3. Vegetation on field or farm boundary areas.Another useful practice is to plant trees and grasses in boundary areas of a farm. Such vegetationprotects soil from run-off by rain and wind; it becomes a source of organic fertilizer, fodder, fuel, food(fruits), or timber, and it also acts as a windbreaker. When flowering plants are used, they may attractnatural enemies such as hoverflies, and provide shelter for natural enemies such as spiders.4. No use of pesticides on soil.<strong>Pest</strong>icides disturb the activity of micro-organisms in the soil and may create imbalances in soil fertility.5. No / Low use of chemical fertilizers.When large amounts of organic material are supplied to the soil every year, usually no chemicalfertilizers need be added. Chemical fertilizers may create an imbalance in the soil ecosystem. Theydisturb the activity of micro-organisms by adding only a few nutrients. In addition, nutrient supply (e.g.too much nitrogen) has been known to cause disease problems in plants. Nonetheless, in somecases it can be good to use a small amount of fertilizer (e.g. nitrogen) to push plants through astressful period.19<strong>Eggplant</strong> Ecological Guide
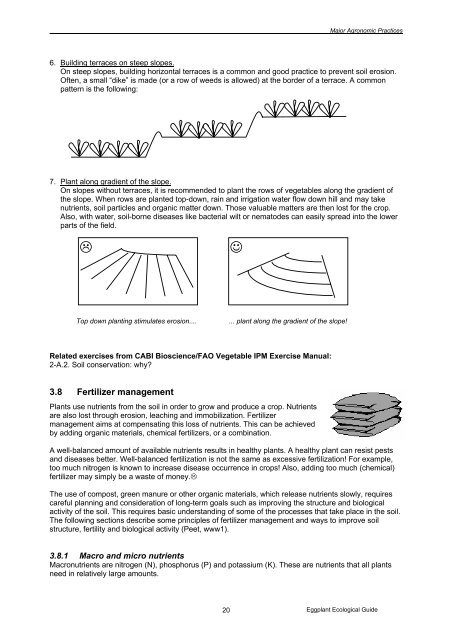
___________________________________________________________________________________Major Agronomic Practices6. Building terraces on steep slopes.On steep slopes, building horizontal terraces is a common and good practice to prevent soil erosion.Often, a small “dike” is made (or a row of weeds is allowed) at the border of a terrace. A commonpattern is the following:7. Plant along gradient of the slope.On slopes without terraces, it is recommended to plant the rows of vegetables along the gradient ofthe slope. When rows are planted top-down, rain and irrigation water flow down hill and may takenutrients, soil particles and organic matter down. Those valuable matters are then lost for the crop.Also, with water, soil-borne diseases like bacterial wilt or nematodes can easily spread into the lowerparts of the field.☺Top down planting stimulates erosion....... plant along the gradient of the slope!Related exercises from CABI Bioscience/FAO Vegetable IPM Exercise Manual:2-A.2. Soil conservation: why?3.8 Fertilizer managementPlants use nutrients from the soil in order to grow and produce a crop. Nutrientsare also lost through erosion, leaching and immobilization. Fertilizermanagement aims at compensating this loss of nutrients. This can be achievedby adding organic materials, chemical fertilizers, or a combination.A well-balanced amount of available nutrients results in healthy plants. A healthy plant can resist pestsand diseases better. Well-balanced fertilization is not the same as excessive fertilization! For example,too much nitrogen is known to increase disease occurrence in crops! Also, adding too much (chemical)fertilizer may simply be a waste of money.The use of compost, green manure or other organic materials, which release nutrients slowly, requirescareful planning and consideration of long-term goals such as improving the structure and biologicalactivity of the soil. This requires basic understanding of some of the processes that take place in the soil.The following sections describe some principles of fertilizer management and ways to improve soilstructure, fertility and biological activity (Peet, www1).3.8.1 Macro and micro nutrientsMacronutrients are nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and potassium (K). These are nutrients that all plantsneed in relatively large amounts.20<strong>Eggplant</strong> Ecological Guide



![Section 4 [ PDF file, 252 KB] - The Field Alliance](https://img.yumpu.com/51387260/1/158x260/section-4-pdf-file-252-kb-the-field-alliance.jpg?quality=85)











